Predicting therapeutic and side effects from drug binding affinities to human proteome structures
- PMID: 38868195
- PMCID: PMC11167438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110032
Predicting therapeutic and side effects from drug binding affinities to human proteome structures
Abstract
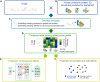
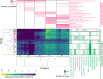
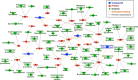
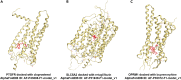
Evaluation of the binding affinities of drugs to proteins is a crucial process for identifying drug pharmacological actions, but it requires three dimensional structures of proteins. Herein, we propose novel computational methods to predict the therapeutic indications and side effects of drug candidate compounds from the binding affinities to human protein structures on a proteome-wide scale. Large-scale docking simulations were performed for 7,582 drugs with 19,135 protein structures revealed by AlphaFold (including experimentally unresolved proteins), and machine learning models on the proteome-wide binding affinity score (PBAS) profiles were constructed. We demonstrated the usefulness of the method for predicting the therapeutic indications for 559 diseases and side effects for 285 toxicities. The method enabled to predict drug indications for which the related protein structures had not been experimentally determined and to successfully extract proteins eliciting the side effects. The proposed method will be useful in various applications in drug discovery.
Keywords: Biocomputational method; Bioinformatics; Biological sciences; Natural sciences; Pharmacoinformatics.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PISTON: Predicting drug indications and side effects using topic modeling and natural language processing.J Biomed Inform. 2018 Nov;87:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.09.015. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Biomed Inform. 2018. PMID: 30268842
-
Predicting Human Clinical Outcomes Using Mouse Multi-Organ Transcriptome.iScience. 2020 Feb 21;23(2):100791. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.100791. Epub 2020 Jan 9. iScience. 2020. PMID: 31928967 Free PMC article.
-
How accurately can one predict drug binding modes using AlphaFold models?Elife. 2023 Dec 22;12:RP89386. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89386. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38131311 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Crystallographic Data for the Development of Machine Learning Models to Predict Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity.Curr Med Chem. 2021 Oct 27;28(34):7006-7022. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210210121320. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33568025 Review.
-
Proteome-scale docking: myth and reality.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013 Sep;10(3):e403-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2013.01.003. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013. PMID: 24050137 Review.
Cited by
-
In-silico evaluation of diffractaic acid as novel anti-diabetic inhibitor against dipeptidyl peptidase IV enzyme.In Silico Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;13(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s40203-025-00321-9. eCollection 2025. In Silico Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944121
-
Proteome-Wide Identification and Comparison of Drug Pockets for Discovering New Drug Indications and Side Effects.Molecules. 2025 Jan 10;30(2):260. doi: 10.3390/molecules30020260. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39860130 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of terminated and withdrawn clinical trials for the treatment and prevention of oral mucositis.J Clin Transl Sci. 2025 Apr 10;9(1):e86. doi: 10.1017/cts.2025.65. eCollection 2025. J Clin Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40384757 Free PMC article.
-
ProteinReDiff: Complex-based ligand-binding proteins redesign by equivariant diffusion-based generative models.Struct Dyn. 2024 Nov 25;11(6):064102. doi: 10.1063/4.0000271. eCollection 2024 Nov. Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 39629167 Free PMC article.
-
The Quantum Paradox in Pharmaceutical Science: Understanding Without Comprehending-A Centennial Reflection.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 13;26(10):4658. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104658. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DiMasi J.A., Grabowski H.G. The cost of biopharmaceutical R&D: is biotech different? MDE. Manage. Decis. Econ. 2007;28:469–479. doi: 10.1002/mde.1360. - DOI
-
- Amano Y., Honda H., Sawada R., Nukada Y., Yamane M., Ikeda N., Morita O., Yamanishi Y. In silico systems for predicting chemical-induced side effects using known and potential chemical protein interactions, enabling mechanism estimation. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020;45:137–149. doi: 10.2131/jts.45.137. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

