Ciliogenesis defects after neurulation impact brain development and neuronal activity in larval zebrafish
- PMID: 38868197
- PMCID: PMC11167523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110078
Ciliogenesis defects after neurulation impact brain development and neuronal activity in larval zebrafish
Abstract
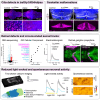
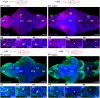
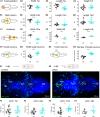
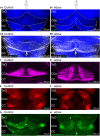
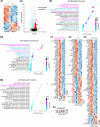
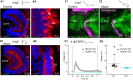
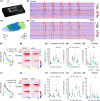
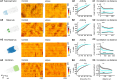
Cilia are slender, hair-like structures extending from cell surfaces and playing essential roles in diverse physiological processes. Within the nervous system, primary cilia contribute to signaling and sensory perception, while motile cilia facilitate cerebrospinal fluid flow. Here, we investigated the impact of ciliary loss on neural circuit development using a zebrafish line displaying ciliogenesis defects. We found that cilia defects after neurulation affect neurogenesis and brain morphology, especially in the cerebellum, and lead to altered gene expression profiles. Using whole brain calcium imaging, we measured reduced light-evoked and spontaneous neuronal activity in all brain regions. By shedding light on the intricate role of cilia in neural circuit formation and function in the zebrafish, our work highlights their evolutionary conserved role in the brain and sets the stage for future analysis of ciliopathy models.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Developmental neuroscience; Neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gopalakrishnan J., Feistel K., Friedrich B.M., Grapin-Botton A., Jurisch-Yaksi N., Mass E., Mick D.U., Müller R.U., May-Simera H., Schermer B., et al. Emerging principles of primary cilia dynamics in controlling tissue organization and function. EMBO J. 2023;42 doi: 10.15252/embj.2023113891. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

