Benign Spindle Cell Lesion of the Nasal Cavity: A Rare Presentation of Solitary Fibrous Tumor
- PMID: 38868242
- PMCID: PMC11168749
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60220
Benign Spindle Cell Lesion of the Nasal Cavity: A Rare Presentation of Solitary Fibrous Tumor
Abstract
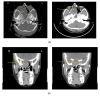
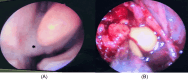
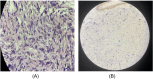
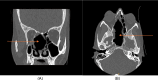
Solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) are rare neoplasms primarily found in the pleural region but have been documented in diverse extrapleural sites, including the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, albeit infrequently. Here, we present a case of a 48-year-old female who presented with a right-sided nasal mass and associated ophthalmologic symptoms, ultimately diagnosed with a benign spindle cell lesion localized to the nasal cavity. The patient underwent a comprehensive evaluation involving clinical examination, radiological imaging, and histopathological analysis, leading to the identification of a benign solitary fibrous tumor. Notably, diagnosing SFTs in the nasal cavity presents challenges due to their nonspecific clinical and imaging features, necessitating a multidisciplinary approach for accurate diagnosis and optimal management. Surgical excision, preferably via endoscopic techniques, remains the cornerstone of treatment based on tumor characteristics and extent. This case underscores the importance of recognizing uncommon presentations of sinonasal lesions, navigating diagnostic complexities, and emphasizing the critical role of multidisciplinary collaboration in achieving favorable treatment outcomes for patients with such nasal cavity tumors.
Keywords: carcinoma; diagnostic nasal endoscopy; excision; lesion; nasal cavity; spindle cell.
Copyright © 2024, Vijayasundaram et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic resection of solitary fibrous tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses.Skull Base. 2011 Mar;21(2):129-34. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1275259. Skull Base. 2011. PMID: 22451814 Free PMC article.
-
Solitary Fibrous Tumour: A Rare Differential Diagnosis of Unilateral Nasal Mass.Cureus. 2023 Mar 30;15(3):e36901. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36901. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37128528 Free PMC article.
-
[Solitary fibrous tumor of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and anterior fossa].Otolaryngol Pol. 2008;62(3):335-9. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6657(08)70266-X. Otolaryngol Pol. 2008. PMID: 18652161 Polish.
-
Solitary fibrous tumour of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.Acta Otolaryngol. 2003 Jan;123(1):71-4. doi: 10.1080/003655402000028052. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003. PMID: 12625577 Review.
-
Sinonasal Tract Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Clinicopathologic Study of Six Cases with a Comprehensive Review of the Literature.Head Neck Pathol. 2018 Dec;12(4):471-480. doi: 10.1007/s12105-017-0878-y. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Head Neck Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29282671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solitary fibrous tumor of nasal cavity: a case report. Mathew GA, Ashish G, Tyagi AK, Chandrashekharan R, Paul RR. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4710884/pdf/ijo-27-307.pdf. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;27:307–312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Solitary fibrous tumor of the nasal cavity. Kessler Kessler, A. A., Lapinsky Lapinsky, J. J., Berenholz Berenholz, L. L., Sarfaty Sarfaty. https://doi.org/10.1053/hn.1999.v121.a95230 Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 1999:826–828. - PubMed
-
- Localized benign and malignant fibrous tumors of the pleura. A clinicopathologic review of 223 cases. England DM, Hochholzer L, McCarthy MJ. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:640–658. - PubMed
-
- Solitary fibrous tumors of the pleura. de Perrot M, Fischer S, Bründler MA, Sekine Y, Keshavjee S. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Solitary fibrous tumor of the orbit. Dorfman DM, To K, Dickersin GR, Rosenberg AE, Pilch BZ. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:281–287. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
