TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 genes expression datasets in COVID-19 patients: Influences of the disease severity and gender
- PMID: 38868379
- PMCID: PMC11166686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110498
TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 genes expression datasets in COVID-19 patients: Influences of the disease severity and gender
Abstract
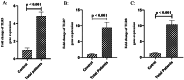
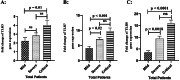
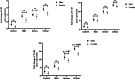
The prognosis of COVID-19 could influence by innate immune sensors such as toll-like receptors (TLRs). The purpose of this data was to investigate TLR3, 7, and 8 expression levels in COVID-19 patients and their relationship to outcome of disease. 75 confirm COVID-19 were included sequentially and separated into three groups: mild, severe, and critical. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from the whole blood, and RNA was then extracted. The qRT-PCR technique was used to examine the expression of TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 genes. The patients average ages were 52.69 ± 1.9 and 13 of the 25 individuals in each group were male. TLR3 (p < 0.001), TLR7 (p < 0.001), and TLR8 (p < 0.001) expression levels were considerably greater in COVID-19 patients compared to the control group. The findings also showed that individuals with critical and severe COVID-19 disease had significantly greater TLR7 and TLR8 gene expression levels than patients in mild stage of disease (p < 0.05). The data showed a significant difference (p = 0.01) in the TLR3 transcript levels between critical and mild COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, male severe (p = 0.02) and critical (p = 0.008) patients had significantly higher TLR8 expression levels than female patients in terms of gender. TLR3 (p = 0.2) and TLR7 (p = 0.08) transcripts were more elevated in males than females, but not significantly.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TLR7; TLR8; Toll-like receptors 3 (TLR3).
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of toll-like receptor agonists and SARS-CoV-2 antigens on interferon (IFN) expression by peripheral blood CD3+ T cells from COVID-19 patients.Exp Mol Pathol. 2024 Jun;137:104897. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2024.104897. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Exp Mol Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38691979
-
Endosomal TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 control neuronal morphology through different transcriptional programs.J Cell Biol. 2018 Aug 6;217(8):2727-2742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201712113. Epub 2018 May 18. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29777026 Free PMC article.
-
The association of single nucleotide polymorphisms of Toll-like receptor 3, Toll-like receptor 7 and Toll-like receptor 8 genes with the susceptibility to HCV infection.Br J Biomed Sci. 2018 Oct;75(4):175-181. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2018.1492186. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Br J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29947302
-
Human Toll-like receptor-dependent induction of interferons in protective immunity to viruses.Immunol Rev. 2007 Dec;220(1):225-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00564.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17979850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression Patterns of Toll-like Receptors in COVID-19 Patients.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Nov 28;28(11):307. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2811307. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 38062845 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering TLR and JAK/STAT pathways: genetic variants and targeted therapies in COVID-19.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 18;52(1):733. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10843-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40679664 Review.
References
-
- Arefinia N., Ghoreshi Z.-S., Alipour A.H., Reza Molaei H., Samie M., Sarvari J. Gastrointestinal Manifestations in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Iran J. Med. Microbiol. 2022;16(4):271–281.
-
- Ghoreshi Z., Nakhaee M., Samie M., Zak M.S., Arefinia N. Innate immune sensors for detecting nucleic acids during infection. LaboratoriumsMedizin. 2022
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

