IRX5's influence on macrophage polarization and outcome in papillary thyroid cancer
- PMID: 38868535
- PMCID: PMC11167072
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399484
IRX5's influence on macrophage polarization and outcome in papillary thyroid cancer
Abstract
Background: With a rise in recent years, thyroid cancer (TC) is the most prevalent hormonal cancer worldwide. It is essential to investigate the inherent variability at the molecular level and the immune environment within tumors of various thyroid cancer subtypes in order to identify potential targets for therapy and provide precise treatment for patients with thyroid adenocarcinoma.
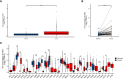
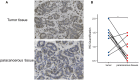
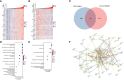
Methods: First, we analyzed the expression of IRX5 in pan-cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma by bioinformatics methods and collected paired samples from our center for validation. Subsequently, we analyzed the significance of IRX5 on the prognosis and diagnosis of PTC. Next, we explored the possible mechanisms by which IRX5 affects the prognosis of thyroid cancer patients by GO/KEGG enrichment analysis, and further investigated the effect of IRX5 on immune infiltration of thyroid cancer. Ultimately, by conducting experiments on cells and animals, we were able to show how IRX5 impacts the aggressive characteristics of thyroid cancer cells and its influence on macrophages within the immune system of thyroid cancer.
Results: In 11 malignant tumors, including PTC, IRX5 is overexpressed and associated with a poor prognosis. IRX5 may affect the prognosis of PTC through embryonic organ development, ossification, mesenchyme development, etc. Increased IRX5 expression decreases the presence of cytotoxic and Th17 cells in papillary thyroid cancer. IRX5 was highly expressed in different PTC cell lines, such as K-1 and TPC-1. Silencing IRX5 effectively halted the growth and movement of PTC cells while also decreasing M2 polarization and enhancing M1 polarization in tumor-associated macrophages.
Conclusion: IRX5 could impact the outlook of individuals with PTC by stimulating the shift of macrophages to M2 in the immune surroundings of thyroid cancer growths, suggesting a potential new focus for treating thyroid cancer, particularly through immunotherapy.
Keywords: IRX5 gene; macrophage polarization; proliferation; thyroid cancer; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Qin, Chen, Gui and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Immune Cell Confrontation in the Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Microenvironment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 22;11:570604. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.570604. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33193087 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ferroptosis genes in immune infiltration and prognosis in thyroid papillary carcinoma using network analysis.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jul 27;22(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07895-6. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34315405 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide reprograms macrophages via the GLP-1R/PPARG/ACSL1 pathway to suppress papillary thyroid carcinoma growth.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Feb 5:dgaf053. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf053. Online ahead of print. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39908200
-
Bleomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in TPC-1 cells through reversing M2-macrophages polarization.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3858-3866. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9103. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127999 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of LPAR5 gene in prognosis and immunity of thyroid papillary carcinoma and pan-cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 10;13(1):5850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32733-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37037831 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Application of microRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Oct 15;17:4681-4699. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S487239. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39429957 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Cancer-The Tumor Immune Microenvironment (TIME) over Time and Space.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;17(5):794. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050794. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

