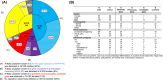
Exome sequencing identifies a likely causative variant in 53% of families with ciliopathy-related features on renal ultrasound after excluding NPHP1 deletions
- PMID: 38868576
- PMCID: PMC11167256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101111
Exome sequencing identifies a likely causative variant in 53% of families with ciliopathy-related features on renal ultrasound after excluding NPHP1 deletions
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

