Game-related behaviors among children and adolescents after school closure during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38868689
- PMCID: PMC11114390
- DOI: 10.1002/pcn5.37
Game-related behaviors among children and adolescents after school closure during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Aim: Increased exposure to digital gaming content among youth in recent years has raised serious health concerns. Social restrictions such as school closures, imposed worldwide because of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, may increase exposure to gaming and lead to addictive gaming behavior in young people. In this study, we investigated gaming behaviors among Japanese students during COVID-19 school closures.
Methods: Students completed questionnaires regarding their living conditions, game-related behaviors, diagnosis of Internet addiction, psychological difficulties, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. We compared differences between the responses of potentially at risk for gaming disorder (potentially at risk for gaming disorder; defined in this paper with reference to the ICD-11 MMS criteria for gaming disorder [PGD]) students who met the criteria for a diagnosis of gaming disorder in ICD-11 MMS and those of control students. Logistic regression analysis was performed to predict the extent of factors contributing to potential gaming disorder.
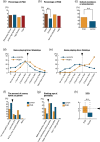
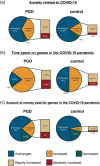
Results: Four thousand and forty-eight participants completed the survey. Compared with control students (93%), potentially at risk for gaming disorder (defined in this paper with reference to the ICD-11 MMS criteria for gaming disorder, PGD) students (7%) reported playing games for longer times, spending more money on in-game purchases, were of younger age at the start of game playing, showed a tendency toward Internet dependence, practised school avoidance or absenteeism, and demonstrated the need for psychological support. Moreover, participants in the PGD group reported more anxiety about COVID-19 than control participants, as well as an increase in game-playing time and amount of money spent on games during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: These results indicate that young people classified as having a gaming disorder not only exhibit characteristic game-related behaviors but may be psychologically and socially vulnerable and need special support, especially during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID‐19; ICD‐11; addictive behavior; anxiety; gaming disorder.
© 2022 The Authors. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leisure and Problem Gaming Behaviors Among Children and Adolescents During School Closures Caused by COVID-19 in Hong Kong: Quantitative Cross-sectional Survey Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 May 7;9(2):e26808. doi: 10.2196/26808. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 33960954 Free PMC article.
-
Addictive Internet Gaming Usage among Korean Adolescents before and after the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison of the Latent Profiles in 2018 and 2020.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 7;18(14):7275. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147275. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299725 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the impact of COVID-19 on the game addiction of children and adolescents.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Aug 18;13:976601. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.976601. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36061296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-Related Social Isolation, Self-Control, and Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese University Students: Cross-Sectional Survey.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 10;26:e52978. doi: 10.2196/52978. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39255486 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Gaming Disorder and Aggression among Students on School Closure during COVID-19 Pandemic.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2022 Jun 2;20(1):41-46. doi: 10.33314/jnhrc.v20i01.3737. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2022. PMID: 35945851
Cited by
-
Investigating the interplay between gaming disorder and functional impairments in professional esports gaming.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 19;14(1):6557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56358-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38503756 Free PMC article.
-
Elementary School Children's Lifestyles in Toyama, Japan, Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Glob Pediatr Health. 2024 Oct 6;11:2333794X241281473. doi: 10.1177/2333794X241281473. eCollection 2024. Glob Pediatr Health. 2024. PMID: 39381791 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Statista . Average number of new iOS app releases per month as of December 2021. Dec 2021. [cited 2022 Mar 11]. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/276705/ios-app-releases-worldwide/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
