Long-term in vivo dissolution of thermo- and pH-responsive, 19F magnetic resonance-traceable and injectable polymer implants
- PMID: 38868824
- PMCID: PMC11166117
- DOI: 10.1039/d4na00212a
Long-term in vivo dissolution of thermo- and pH-responsive, 19F magnetic resonance-traceable and injectable polymer implants
Abstract
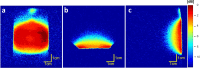
19F magnetic resonance (19F MR) tracers stand out for their wide range of applications in experimental and clinical medicine, as they can be precisely located in living tissues with negligible fluorine background. This contribution demonstrates the long-term dissolution of multiresponsive fluorinated implants designed for prolonged release. Implants were detected for 14 (intramuscular injection) and 20 (subcutaneous injection) months by 19F MR at 4.7 T, showing favorable MR relaxation times, biochemical stability, biological compatibility and slow, long-term dissolution. Thus, polymeric implants may become a platform for long-term local theranostics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Implant-forming polymeric 19F MRI-tracer with tunable dissolution.J Control Release. 2020 Nov 10;327:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.026. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32730953
-
Peptidic Monodisperse PEG "Comb" as Multifunctional "Add-On" Module for Imaging-Traceable and Thermo-Responsive Theranostics.Adv Healthc Mater. 2020 Feb;9(3):e1901331. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901331. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020. PMID: 31851435
-
Self-Assembled Fluorinated Nanoparticles as Sensitive and Biocompatible Theranostic Platforms for 19F MRI.Macromol Biosci. 2024 Jun;24(6):e2300510. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300510. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Macromol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38217510
-
19F Magnetic Resonance Activity-Based Sensing Using Paramagnetic Metals.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Jan 21;53(1):2-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00352. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31809009 Review.
-
Targeted, Stimuli-Responsive, and Theranostic 19F Magnetic Resonance Imaging Probes.Bioconjug Chem. 2019 Oct 16;30(10):2502-2518. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00582. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Bioconjug Chem. 2019. PMID: 31536323 Review.
Cited by
-
Stimuli-Responsive Polymers for Advanced 19F Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Chemical Design to Biomedical Applications.Biomacromolecules. 2024 Sep 9;25(9):5630-5649. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00833. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Biomacromolecules. 2024. PMID: 39151065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Water-soluble fluorinated copolymers as highly sensitive 19F MRI tracers: From structure optimization to multimodal tumor imaging.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jan 4;31:101462. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101462. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 39896294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kostiv U. Natile M. M. Jirák D. Půlpánová D. Jiráková K. Vosmanská M. et al., Peg-neridronate-modified NaYf4:GD3+,Yb3+,TM3+/NaGdf4 core–shell upconverting nanoparticles for bimodal magnetic resonance/optical luminescence imaging. ACS Omega. 2021;6:14420–14429. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01313. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01313. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kracíková L. Ziółkowska N. Androvič L. Klimánková I. Červený D. Vít M. et al., Phosphorus-containing Polymeric Zwitterion: a pioneering bioresponsive probe for 31 p-magnetic resonance imaging. Macromol. Biosci. 2022:2100523. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202100523. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202100523. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

