Staphylococcal aconitase expression during iron deficiency is controlled by an sRNA-driven feedforward loop and moonlighting activity
- PMID: 38869061
- PMCID: PMC11317140
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae506
Staphylococcal aconitase expression during iron deficiency is controlled by an sRNA-driven feedforward loop and moonlighting activity
Abstract
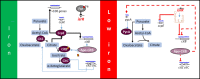
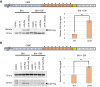
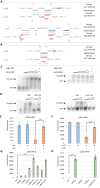
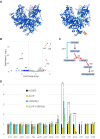
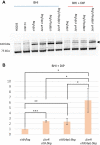
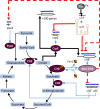
Pathogenic bacteria employ complex systems to cope with metal ion shortage conditions and propagate in the host. IsrR is a regulatory RNA (sRNA) whose activity is decisive for optimum Staphylococcus aureus fitness upon iron starvation and for full virulence. IsrR down-regulates several genes encoding iron-containing enzymes to spare iron for essential processes. Here, we report that IsrR regulates the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle by controlling aconitase (CitB), an iron-sulfur cluster-containing enzyme, and its transcriptional regulator, CcpE. This IsrR-dependent dual-regulatory mechanism provides an RNA-driven feedforward loop, underscoring the tight control required to prevent aconitase expression. Beyond its canonical enzymatic role, aconitase becomes an RNA-binding protein with regulatory activity in iron-deprived conditions, a feature that is conserved in S. aureus. Aconitase not only negatively regulates its own expression, but also impacts the enzymes involved in both its substrate supply and product utilization. This moonlighting activity concurrently upregulates pyruvate carboxylase expression, allowing it to compensate for the TCA cycle deficiency associated with iron scarcity. These results highlight the cascade of complex posttranscriptional regulations controlling S. aureus central metabolism in response to iron deficiency.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Dutta T., Srivastava S.. Small RNA-mediated regulation in bacteria: a growing palette of diverse mechanisms. Gene. 2018; 656:60–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

