Intracellular Osteopontin Promotes the Release of TNFα by Mast Cells to Restrain Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38869181
- PMCID: PMC11369624
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0792
Intracellular Osteopontin Promotes the Release of TNFα by Mast Cells to Restrain Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer
Abstract
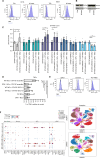
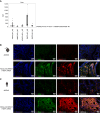
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) is an aggressive form of prostate cancer that emerges as tumors become resistant to hormone therapies or, rarely, arises de novo in treatment-naïve patients. The urgent need for effective therapies against NEPC is hampered by the limited knowledge of the biology governing this lethal disease. Based on our prior observations in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) spontaneous prostate cancer model, in which the genetic depletion of either mast cells (MC) or the matricellular protein osteopontin (OPN) increases NEPC frequency, we tested the hypothesis that MCs can restrain NEPC through OPN production, using in vitro co-cultures between murine or human tumor cell lines and MCs, and in vivo experiments. We unveiled a role for the intracellular isoform of OPN, so far neglected compared with the secreted isoform. Mechanistically, we unraveled that the intracellular isoform of OPN promotes TNFα production in MCs via the TLR2/TLR4-MyD88 axis, specifically triggered by the encounter with NEPC cells. We found that MC-derived TNFα, in turn, hampered the growth of NEPC. We then identified the protein syndecan-1 (SDC1) as the NEPC-specific TLR2/TLR4 ligand that triggered this pathway. Interrogating published single-cell RNA-sequencing data, we validated this mechanism in a different mouse model. Translational relevance of the results was provided by in silico analyses of available human NEPC datasets and by immunofluorescence on patient-derived adenocarcinoma and NEPC lesions. Overall, our results show that MCs actively inhibit NEPC, paving the way for innovative MC-based therapies for this fatal tumor. We also highlight SDC1 as a potential biomarker for incipient NEPC.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
E. Jachetti reports grants from Italian Ministry of Health and grants from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

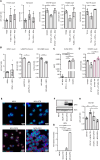
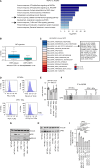
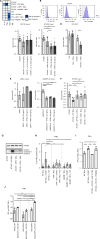
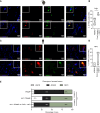
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Chedgy EC, Vandekerkhove G, Herberts C, Annala M, Donoghue AJ, Sigouros M, et al. Biallelic tumour suppressor loss and DNA repair defects in de novo small-cell prostate carcinoma. J Pathol 2018;246:244–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

