Isolation and Identification of Novel Taste-Modulating N2-Guanosine 5'-Monophosphate Derivatives Generated by Maillard-Type Reactions
- PMID: 38869215
- PMCID: PMC11212044
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c03485
Isolation and Identification of Novel Taste-Modulating N2-Guanosine 5'-Monophosphate Derivatives Generated by Maillard-Type Reactions
Abstract
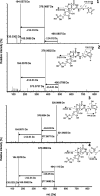
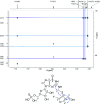
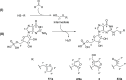
Several compounds with taste-modulating properties have been investigated, improving the taste impression without having a pronounced intrinsic taste. The best-known representatives of umami taste-modulating compounds are ribonucleotides and their derivatives. Especially the thio derivatives showed high taste-modulating potential in structure-activity relationship investigations. Therefore, this study focuses on the formation of guanosine 5'-monophosphate derivatives consisting of Maillard-type generated compounds like the aroma-active thiols (2-methyl-3-furanthiol, 3-mercapto-2-pentanone, 2-furfurylthiol) and formaldehyde to gain insights into the potential of combinations of taste and aroma-active compounds. One literature-known (N2-(furfurylthiomethyl)-guanosine 5'-monophosphate) and three new derivatives (N2-(2-methyl-1-furylthiomethyl)-guanosine 5'-monophosphate, N2-((5-hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-1-furylthiomethyl)-guanosine 5'-monophosphate, N2-((2-pentanon-1-yl)thiomethyl)-guanosine 5'-monophosphate) were successfully produced using green natural deep eutectic solvents and isolated, and their structures were completely elucidated. Besides the intrinsic taste properties, the kokumi and umami taste-modulating effects of the four derivatives were evaluated via psychophysical investigations, ranging from 19 to 22 μmol/L.
Keywords: 2-methyl-3-furanthiol; Maillard-type model reactions; guanosine 5′-monophosphate derivatives; taste modulating; umami.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human taste and umami receptor responses to chemosensorica generated by Maillard-type N²-alkyl- and N²-arylthiomethylation of guanosine 5'-monophosphates.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Nov 26;62(47):11429-40. doi: 10.1021/jf504686s. Epub 2014 Nov 17. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 25375264
-
Novel Taste-Enhancing 4-Amino-2-methyl-5-heteroalkypyrimidines Formed from Thiamine by Maillard-Type Reactions.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Dec 18;67(50):13986-13997. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05896. Epub 2019 Dec 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31710220
-
Systematic studies on the chemical structure and umami enhancing activity of Maillard-modified guanosine 5'-monophosphates.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jan 26;59(2):665-76. doi: 10.1021/jf103849e. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21162577
-
The umami taste: from discovery to clinical use.Otolaryngol Pol. 2016 Jun 30;70(4):10-5. doi: 10.5604/00306657.1199991. Otolaryngol Pol. 2016. PMID: 27387211 Review.
-
Umami the Fifth Basic Taste: History of Studies on Receptor Mechanisms and Role as a Food Flavor.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:189402. doi: 10.1155/2015/189402. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26247011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cappuccio F. P.Accelerating Salt Reduction in Europe: A Country Support Package to Reduce Population Salt Intake in the WHO European Region, World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe; 2020.
-
- Panel E.; Mortensen A.; Aguilar F.; Crebelli R.; Di Domenico A.; Dusemund B.; Frutos M. J.; Galtier P.; Gott D.; Gundert-Remy U.; et al. Re-evaluation of glutamic acid (E 620), sodium glutamate (E 621), potassium glutamate (E 622), calcium glutamate (E 623), ammonium glutamate (E 624) and magnesium glutamate (E 625) as food additives. EFSA J. 2017, 15 (7), e0491010.2903/j.efsa.2017.4910. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

