LncRNA KIFAP3-5:1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular cell through PRRX1 in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 38869718
- PMCID: PMC11176233
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-024-09874-5
LncRNA KIFAP3-5:1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular cell through PRRX1 in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
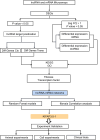
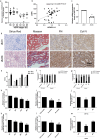
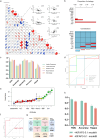
Long noncoding RNAs play an important role in several pathogenic processes in diabetic nephropathy, but the relationship with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in DN is unclear. Herein, we found that KIFAP3-5:1 expression was significantly down-regulated in DN plasma samples, db/db mouse kidney tissues and high glucose treated renal tubular epithelial cells compared to normal healthy samples and untreated cells. Overexpression of KIFAP3-5:1 improved renal fibrosis in db/db mice and rescued epithelial-mesenchymal transition of high glucose cultured renal tubular epithelial cells. The silence of KIFAP3-5:1 will exacerbate the progression of EMT. Mechanistically, KIFAP3-5:1 was confirmed to directly target to the -488 to -609 element of the PRRX1 promoter and negatively modulate PRRX1 mRNA and protein expressions. Furthermore, rescue assays demonstrated that the knockdown of PRRX1 counteracted the KIFAP3-5:1 low expression-mediated effects on EMT in hRPTECs cultured under high glucose. The plasma KIFAP3-5:1 of DN patients is highly correlated with the severity of renal dysfunction and plays an important role in the prediction model of DN diseases. These findings suggested that KIFAP3-5:1 plays a critical role in regulation of renal EMT and fibrosis through suppress PRRX1, and highlight the clinical potential of KIFAP3-5:1 to assist in the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; EMT, renal fibrosis; KIFAP3-5:1; PRRX1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Chrysin inhibits diabetic renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis through blocking epithelial to mesenchymal transition.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Jul;93(7):759-72. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1301-3. Epub 2015 Jun 11. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26062793
-
Effects and mechanism of miR-23b on glucose-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jan;70:149-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26646104
-
Inactivation of TSC1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells in mouse diabetic nephropathy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Dec;40(12):1555-1567. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0244-6. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31235817 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt1 inhibits renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition through YY1 deacetylation in diabetic nephropathy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Feb;42(2):242-251. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0450-2. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 32555442 Free PMC article.
-
miR-30b-5p modulate renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy by directly targeting SNAI1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 8;535:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.096. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33383483
Cited by
-
Stress-Related LncRNAs and Their Roles in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2194. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052194. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Block CJ, Mitchell AV, Wu L, Glassbrook J, Craig D, Chen W, Dyson G, DeGracia D, Polin L, Ratnam M, Gibson H, Wu G. RNA binding protein RBMS3 is a common EMT effector that modulates triple-negative breast cancer progression via stabilizing PRRX1 mRNA. Oncogene. 2021;46:6430–42. 10.1038/s41388-021-02030-x. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bosada FM, Rivaud MR, Uhm JS, Verheule S, van Duijvenboden K, Verkerk AO, Christoffels VM, Boukens BJ. A variant noncoding region regulates prrx1 and predisposes to atrial arrhythmias. Circ Res. 2021;3:420–34. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319146. - PubMed
-
- Bridoux F, Leung N, Belmouaz M, Royal V, Ronco P, Nasr SH, Fermand JP. Management of acute kidney injury in symptomatic multiple myeloma. Kidney Int. 2021;3:570–80. 10.1016/j.kint.2020.11.010. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Chen Y, Li Y, Lian W, Zheng K, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Lin C, Liu C, Sun F, Sun X, Wang J, Zhao L, Ke Y. Prrx1 promotes stemness and angiogenesis via activating TGF-beta/smad pathway and upregulating proangiogenic factors in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2021;6:615. 10.1038/s41419-021-03882-7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82003822/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073906/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81973377/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20KJB310022/Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- 19KJA460008/Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

