Compatibility of synthetic and biological pesticides with a biocontrol agent Phytoseiulus longipes (Acari: Phytoseiidae)
- PMID: 38869728
- PMCID: PMC11269511
- DOI: 10.1007/s10493-024-00926-3
Compatibility of synthetic and biological pesticides with a biocontrol agent Phytoseiulus longipes (Acari: Phytoseiidae)
Abstract
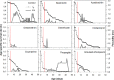
Phytoseiulus longipes is a predatory mite of Tetranychus evansi, which is an invasive pest in Africa and elsewhere. The introduction of this predator in Africa has considerable potential, but little is known about the compatibility of P. longipes with commonly used pesticides. Here, we examined lethal and sublethal effects of two pyrethroids (cypermethrin and deltamethrin), two organophosphates (dimethoate and chlorpyrifos), one nicotinoid (imidacloprid), two acaricides (propargite and abamectin), two naturally derived pesticides (oxymatrine and azadirachtin), and one entomopathogenic fungal-based formulation (Hirsutella thompsonii) on P. longipes eggs and adults. The pesticides were sprayed at their maximum recommended concentrations. Topical exposures to azadirachtin, imidacloprid, propargite, abamectin, oxymatrine, and H. thompsonii significantly reduced the net reproductive rate (R0), intrinsic rate of increase (r) and finite rate of increase (λ)of P. longipes. Pesticide lethal and sublethal effects on the predator were summarized in a reduction coefficient (Ex) for the classification based on IOBC toxicity categories. Results revealed that Azadirachtin and H. thompsonii were slightly harmful effects to adults. Imidacloprid, propargite, abamectin, and oxymatrine were moderately harmful to both eggs and adults. Residual persistence bioassays revealed that 4-day-old residue of azadirachtin had no harmful effect on the predator. Abamectin, oxymatrine, and H. thompsonii became harmless to it 10 days post-spraying, and propargite and imidacloprid were considered harmless after 20 days. Cypermethrin, deltamethrin, dimethoate, and chlorpyrifos were highly harmful to both eggs and adults, persistence remaining high even after 31 days of application. These findings provide valuable insights into decision-making when considering P. longipes for use in IPM programs.
Keywords: Augmentative releases; Conservation biological control; IPM Tetranychus evansi; Pesticide selection; Phytoseid mites; Residual effect.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abad-Moyano R, Pina T, Ferragut F, Urbaneja A (2009) Comparative life-history traits of three phytoseiid mites associated with Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) colonies in clementine orchards in eastern Spain: implications for biological control. Exp Appl Acarol 47:121–132. 10.1007/s10493-008-9197-z 10.1007/s10493-008-9197-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abou-Awad BA, El-Banhawy EM (1985) Comparison between the toxicity of synthetic pyrethroids and other compounds to the predacious mite Amblyseius Gossipi (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 1:185–191. 10.1007/BF0119851510.1007/BF01198515 - DOI
-
- Agrofit (2021) Sistema de Agrotóxicos Fitossanitários - Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento, Brasil. In. http://extranet.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons. Accessed Accessed 14 Jan 2021
-
- Ali S, Zhang C, Wang Z, Wang XM, Wu JH, Cuthbertson AGS, Shao Z, Qiu BL (2017) Toxicological and biochemical basis of synergism between the entomopathogenic fungus lecanicillium muscarium and the insecticide matrine against Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius). Sci Rep 7:46558. 10.1038/srep46558 10.1038/srep46558 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argolo PSBN, Santiago S, Mollá Ó, Jacas JA, Urbaneja A (2013) Compatibility of Phytoseiulus Persimilis and Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) with imidacloprid to manage clementine nursery pests. Crop Prot 43:175–182. 10.1016/j.cropro.2012.09.01810.1016/j.cropro.2012.09.018 - DOI