Unveiling advanced strategies for therapeutic stem cell interventions in severe burn injuries: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 38869979
- PMCID: PMC11487052
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001812
Unveiling advanced strategies for therapeutic stem cell interventions in severe burn injuries: a comprehensive review
Abstract
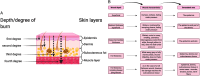
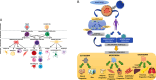
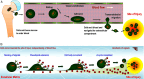
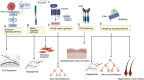
This comprehensive review explores the complex terrain of stem cell therapies as a potential therapeutic frontier in the healing of complicated burn wounds. Serious tissue damage, impaired healing processes, and possible long-term consequences make burn wounds a complex problem. An in-depth review is required since, despite medical progress, existing methods for treating severe burn wounds have significant limitations. Burn wounds are difficult to heal because they cause extensive tissue damage. The challenges of burn injury-induced tissue regeneration and functional recovery are also the subject of this review. Although there is a lot of promise in current stem cell treatments, there are also some limitations with scalability, finding the best way to transport the cells, and finding consistent results across different types of patients. To shed light on how to improve stem cell interventions to heal severe burn wounds, this review covers various stem cell applications in burn wounds and examines these obstacles. To overcome these obstacles, one solution is to enhance methods of stem cell distribution, modify therapies according to the severity of the burn, and conduct more studies on how stem cell therapy affects individual patients. Novel solutions may also be possible through the combination of cutting-edge technologies like nanotechnology and biotechnology. This review seeks to increase stem cell interventions by analyzing present challenges and suggesting strategic improvements. The goal is to provide a more effective and tailored way to repair serious burn wounds.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
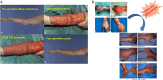
References
-
- Yousef H, Alhajj M, Sharma S, Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Sorg H, Sorg CGG. Skin wound healing: of players, patterns, and processes. Eur Surg Res 2023;64:141–157. - PubMed
-
- Jana S, Datta P, Das H, et al. Engineering vascularizing electrospun dermal grafts by integrating fish collagen and ion-doped bioactive glass. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2022;8:734–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

