Corilagin relieves atherosclerosis via the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 38869980
- PMCID: PMC11179462
- DOI: 10.1177/03946320241254083
Corilagin relieves atherosclerosis via the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Introduction: Corilagin possesses a diverse range of pharmacologic bioactivities. However, the specific protective effects and mechanisms of action of corilagin in the context of atherosclerosis remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the impact of corilagin on the toll-like receptor (TLR)4 signaling pathway in a mouse vascular smooth muscle cell line (MOVAS) stimulated by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL). Additionally, we examined the effects of corilagin in Sprague-Dawley rats experiencing atherosclerosis.
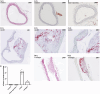
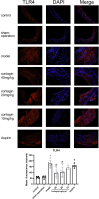
Methods: The cytotoxicity of corilagin was assessed using the CCK8 assay. MOVAS cells, pre-incubated with ox-LDL, underwent treatment with varying concentrations of corilagin. TLR4 expression was modulated by either downregulation through small interfering (si)RNA or upregulation via lentivirus transfection. Molecular expression within the TLR4 signaling pathway was analyzed using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Western blotting. The proliferation capacity of MOVAS cells was determined through cell counting. In a rat model, atherosclerosis was induced in femoral arteries using an improved guidewire injury method, and TLR4 expression in plaque areas was assessed using immunofluorescence. Pathological changes were examined through hematoxylin and eosin staining, as well as Oil-Red-O staining.
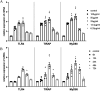
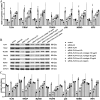
Results: Corilagin demonstrated inhibitory effects on the TLR4 signaling pathway in MOVAS cells pre-stimulated with ox-LDL, consequently impeding the proliferative impact of ox-LDL. The modulation of TLR4 expression, either through downregulation or upregulation, similarly influenced the expression of downstream molecules. In an in vivo context, corilagin exhibited the ability to suppress TLR4 and MyD88 expression in the plaque lesion areas of rat femoral arteries, thereby alleviating the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Conclusion: Corilagin can inhibit the TLR4 signaling pathway in VSMCs, possibly by downregulating TLR4 expression and, consequently, relieving atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; corilagin; ox-LDL; toll-like receptor 4; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

