End-stage renal disease accompanied by mild cognitive impairment: A study and analysis of trimodal brain network fusion
- PMID: 38870175
- PMCID: PMC11175492
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305079
End-stage renal disease accompanied by mild cognitive impairment: A study and analysis of trimodal brain network fusion
Abstract
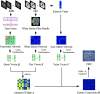
The function and structure of brain networks (BN) may undergo changes in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), particularly in those accompanied by mild cognitive impairment (ESRDaMCI). Many existing methods for fusing BN focus on extracting interaction features between pairs of network nodes from each mode and combining them. This approach overlooks the correlation between different modal features during feature extraction and the potentially valuable information that may exist between more than two brain regions. To address this issue, we propose a model using a multi-head self-attention mechanism to fuse brain functional networks, white matter structural networks, and gray matter structural networks, which results in the construction of brain fusion networks (FBN). Initially, three networks are constructed: the brain function network, the white matter structure network, and the individual-based gray matter structure network. The multi-head self-attention mechanism is then applied to fuse the three types of networks, generating attention weights that are transformed into an optimized model. The optimized model introduces hypergraph popular regular term and L1 norm regular term, leading to the formation of FBN. Finally, FBN is employed in the diagnosis and prediction of ESRDaMCI to evaluate its classification performance and investigate the correlation between discriminative brain regions and cognitive dysfunction. Experimental results demonstrate that the optimal classification accuracy achieved is 92.80%, which is at least 3.63% higher than the accuracy attained using other methods. This outcome confirms the effectiveness of our proposed method. Additionally, the identification of brain regions significantly associated with scores on the Montreal cognitive assessment scale may shed light on the underlying pathogenesis of ESRDaMCI.
Copyright: © 2024 Chen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Foster R, Walker S, Brar R, Hiebert B, Komenda P, Rigatto C, et al. Cognitive Impairment in Advanced Chronic KidneyDiscase: The Canadian Frailty Observation and Interventions Trial. Am J Nephrol. 2016;44: 473–480. - PubMed
-
- Wang SH, Zhang Y, Li YJ, Jia WJ, Liu FY, Yang MM, et al. Single slice based detection for Alzheimer’s disease via wavelet entropy and multilayer perceptron trained by biogeography-based optimization. Multimed Tools Appl. 2018; 77: 10393–10417.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

