Metabolic inflexibility promotes mitochondrial health during liver regeneration
- PMID: 38870309
- PMCID: PMC11232486
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adj4301
Metabolic inflexibility promotes mitochondrial health during liver regeneration
Abstract
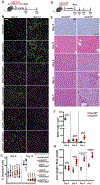
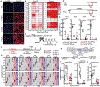
Mitochondria are critical for proper organ function and mechanisms to promote mitochondrial health during regeneration would benefit tissue homeostasis. We report that during liver regeneration, proliferation is suppressed in electron transport chain (ETC)-dysfunctional hepatocytes due to an inability to generate acetyl-CoA from peripheral fatty acids through mitochondrial β-oxidation. Alternative modes for acetyl-CoA production from pyruvate or acetate are suppressed in the setting of ETC dysfunction. This metabolic inflexibility forces a dependence on ETC-functional mitochondria and restoring acetyl-CoA production from pyruvate is sufficient to allow ETC-dysfunctional hepatocytes to proliferate. We propose that metabolic inflexibility within hepatocytes can be advantageous by limiting the expansion of ETC-dysfunctional cells.
Figures





References
-
- Koliaki C. et al., Adaptation of hepatic mitochondrial function in humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver is lost in steatohepatitis. Cell Metab 21, 739–746 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Perez-Carreras M. et al., Defective hepatic mitochondrial respiratory chain in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 38, 999–1007 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Cortez-Pinto H. et al., Alterations in liver ATP homeostasis in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. JAMA 282, 1659–1664 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Fromenty B, Roden M, Mitochondrial alterations in fatty liver diseases. J Hepatol 78, 415–429 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 CA254150/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA239330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 ES030449/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125396/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA277576/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA220449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA142543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR073217/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001104/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK137407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD032267/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028791/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

