Hyperbaric oxygen treatment in bilateral orchiopexy and post-circumcision haematoma in a thrombocytopenic patient with Noonan syndrome
- PMID: 38870956
- PMCID: PMC11444912
- DOI: 10.28920/dhm54.2.133-136
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment in bilateral orchiopexy and post-circumcision haematoma in a thrombocytopenic patient with Noonan syndrome
Abstract
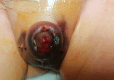
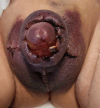
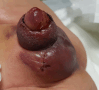
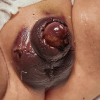
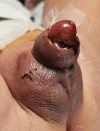
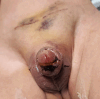
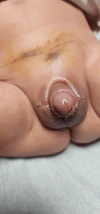
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) can be utilised for necrotising soft tissue infections, clostridial myonecrosis (gas gangrene), crush injuries, acute traumatic ischaemia, delayed wound healing, and compromised skin grafts. Our case was a 17-month-old male patient with Noonan syndrome, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and bilateral undescended testicles. Haematoma and oedema developed in the scrotum and penis the day after bilateral orchiopexy and circumcision. Ischaemic appearances were observed on the penile and scrotal skin on the second postoperative day. Enoxaparin sodium and fresh frozen plasma were started on the recommendation of haematology. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment was initiated considering the possibility of tissue necrosis. We observed rapid healing within five days. We present this case to emphasise that HBOT may be considered as an additional treatment option in patients with similar conditions. To our knowledge, no similar cases have been reported in the literature.
Keywords: Case reports; Children; Haematology; Hyperbaric oxygenation; Injuries; Surgery.
Copyright: This article is the copyright of the authors who grant Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine a non-exclusive licence to publish the article in electronic and other forms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Sahni T, Singh P, John MJ. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: current trends and applications. J Assoc Physicians India. 2003;51:280–4. - PubMed
-
- Jain KK HBO Therapy in infections. In: Jain KK, editor. Textbook of hyperbaric medicine. Switzerland: Springer; 2017. p. 155–70.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
