Utility of carboplatin therapeutic drug monitoring for the treatment of neonate and infant retinoblastoma patients in the United Kingdom
- PMID: 38871807
- PMCID: PMC11300439
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-024-02728-1
Utility of carboplatin therapeutic drug monitoring for the treatment of neonate and infant retinoblastoma patients in the United Kingdom
Abstract
Background: Retinoblastoma is the most common intra-ocular malignancy in children and frequently presents in very young patients who commonly require intravenous carboplatin. Delivering this is challenging due to a lack of uniform dosing recommendations, rapid changes in physiological function and the risk of side-effects.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of neonates and infants in the UK with retinoblastoma, who have undergone carboplatin therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). We report on the pharmacokinetic, treatment efficacy and toxicity data.
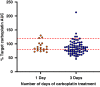
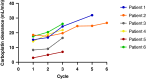
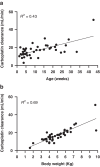
Results: In total, 29 patients (median age 5 weeks at treatment onset) underwent a total of 74 TDM guided cycles of chemotherapy, involving real time sampling and dose adjustment. An additional 13 patients underwent TDM sampling to modify doses between cycles. Without the adoption of TDM guided dosing, carboplatin exposures would have been ≥20% outside the target AUC in 38/78 (49%) of treatment cycles. Excellent responses and a reassuringly low incidence of toxicities were observed following dose adjustment, despite the young patient age and the implementation of dose increases in the majority of cases.
Conclusions: Real time TDM is safe, effective and deliverable for neonates and infants receiving carboplatin for retinoblastoma and should be considered standard of care up to the age of 6 months.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

