Depleting profibrotic macrophages using bioactivated in vivo assembly peptides ameliorates kidney fibrosis
- PMID: 38871810
- PMCID: PMC11291639
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-024-01190-6
Depleting profibrotic macrophages using bioactivated in vivo assembly peptides ameliorates kidney fibrosis
Abstract
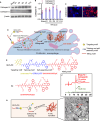
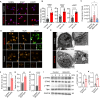
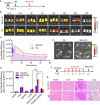
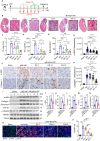
Managing renal fibrosis is challenging owing to the complex cell signaling redundancy in diseased kidneys. Renal fibrosis involves an immune response dominated by macrophages, which activates myofibroblasts in fibrotic niches. However, macrophages exhibit high heterogeneity, hindering their potential as therapeutic cell targets. Herein, we aimed to eliminate specific macrophage subsets that drive the profibrotic immune response in the kidney both temporally and spatially. We identified the major profibrotic macrophage subset (Fn1+Spp1+Arg1+) in the kidney and then constructed a 12-mer glycopeptide that was designated as bioactivated in vivo assembly PK (BIVA-PK) to deplete these cells. BIVA-PK specifically binds to and is internalized by profibrotic macrophages. By inducing macrophage cell death, BIVA-PK reshaped the renal microenvironment and suppressed profibrotic immune responses. The robust efficacy of BIVA-PK in ameliorating renal fibrosis and preserving kidney function highlights the value of targeting macrophage subsets as a potential therapy for patients with CKD.
Keywords: Bioactivated in vivo assembly-PK (BIVA-PK); Renal fibrosis; cell death; immune microenvironment; pro-fibrotic macrophage.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CSI and USTC.
Conflict of interest statement
QO, TS, LLL, and XC are co-inventors on China Invention Patent Application no. ZL 2022 1 0056384.3 filed by the Chinese PLA General Hospital related to the subject matter of this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2021;398:786–802. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Bowe B, Mokdad AH, Xian H, Yan Y, Li T, et al. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018;94:567–81. - PubMed
-
- Foreman KJ, Marquez N, Dolgert A, Fukutaki K, Fullman N, McGaughey M, et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet. 2018;392:2052–90. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

