Optimal design of synthetic circular RNAs
- PMID: 38871815
- PMCID: PMC11263348
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01251-w
Optimal design of synthetic circular RNAs
Abstract
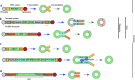
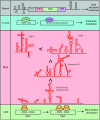
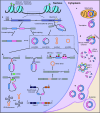
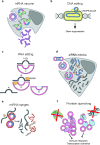
Circular RNAs are an unusual class of single-stranded RNAs whose ends are covalently linked via back-splicing. Due to their versatility, the need to express circular RNAs in vivo and in vitro has increased. Efforts have been made to efficiently and precisely synthesize circular RNAs. However, a review on the optimization of the processes of circular RNA design, synthesis, and delivery is lacking. Our review highlights the multifaceted aspects considered when producing optimal circular RNAs and summarizes the available options for each step of exogenous circular RNA design and synthesis, including circularization strategies. Additionally, this review describes several potential applications of circular RNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

