ADAMTS2 promotes radial migration by activating TGF-β signaling in the developing neocortex
- PMID: 38871984
- PMCID: PMC11239934
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00174-x
ADAMTS2 promotes radial migration by activating TGF-β signaling in the developing neocortex
Abstract
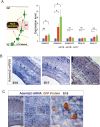
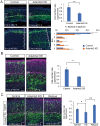
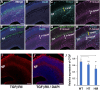
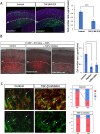
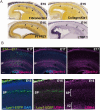
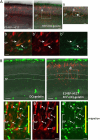
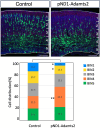
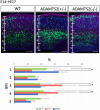
The mammalian neocortex is formed by sequential radial migration of newborn excitatory neurons. Migrating neurons undergo a multipolar-to-bipolar transition at the subplate (SP) layer, where extracellular matrix (ECM) components are abundantly expressed. Here, we investigate the role of the ECM at the SP layer. We show that TGF-β signaling-related ECM proteins, and their downstream effector, p-smad2/3, are selectively expressed in the SP layer. We also find that migrating neurons express a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 2 (ADAMTS2), an ECM metalloproteinase, just below the SP layer. Knockdown and knockout of Adamts2 suppresses the multipolar-to-bipolar transition of migrating neurons and disturbs radial migration. Time-lapse luminescence imaging of TGF-β signaling indicates that ADAMTS2 activates this signaling pathway in migrating neurons during the multipolar-to-bipolar transition at the SP layer. Overexpression of TGF-β2 in migrating neurons partially rescues migration defects in ADAMTS2 knockout mice. Our data suggest that ADAMTS2 secreted by the migrating multipolar neurons activates TGF-β signaling by ECM remodeling of the SP layer, which might drive the multipolar to bipolar transition.
Keywords: ADAMTS2; Cerebral Cortex; ECM; Radial Migration; TGF-β.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bekhouche M, Leduc C, Dupont L, Janssen L, Delolme F, Vadon-Le Goff S, Smargiasso N, Baiwir D, Mazzucchelli G, Zanella-Cleon I, et al. Determination of the substrate repertoire of ADAMTS2, 3, and 14 significantly broadens their functions and identifies extracellular matrix organization and TGF-beta signaling as primary targets. FASEB J. 2016;30:1741–1756. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-279869. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Colige A, Sieron AL, Li SW, Schwarze U, Petty E, Wertelecki W, Wilcox W, Krakow D, Cohn DH, Reardon W, et al. Human Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII C and bovine dermatosparaxis are caused by mutations in the procollagen I N-proteinase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65:308–317. doi: 10.1086/302504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 17K07428/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 19H04795/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 20H03270/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 16K07077/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP21gm1310012/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- Y2018 research grant/Takeda Science Foundation (TSF)
- Y2018 research grant/Naito Foundation ()
- FY2020 research grant/NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for the Promotion of Science (NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan))
- FY2021 research grant/Astellas Pharma (Astellas)
- FY2021 research grant/KOSE Cosmetology Research Foundation
- FY2021 research grant/Mitsubishi Foundation (The Mitsubishi Foundation)
- FY2021 research grant/Yamada Science Foundation (YSF)
- FY2021 research grant/Brain Science Foundation (Japan)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

