A multidomain lifestyle intervention to maintain optimal cognitive functioning in Dutch older adults-study design and baseline characteristics of the FINGER-NL randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38872204
- PMCID: PMC11170777
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01495-8
A multidomain lifestyle intervention to maintain optimal cognitive functioning in Dutch older adults-study design and baseline characteristics of the FINGER-NL randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Evidence on the effectiveness of multidomain lifestyle interventions to prevent cognitive decline in older people without dementia is mixed. Embedded in the World-Wide FINGERS initiative, FINGER-NL aims to investigate the effectiveness of a 2-year multidomain lifestyle intervention on cognitive functioning in older Dutch at risk individuals.
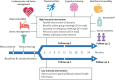
Methods: Multi-center, randomized, controlled, multidomain lifestyle intervention trial with a duration of 24 months. 1210 adults between 60-79 years old with presence of ≥ 2 modifiable risk factors and ≥ 1 non-modifiable risk factor for cognitive decline were recruited between January 2022 and May 2023 via the Dutch Brain Research Registry and across five study sites in the Netherlands. Participants were randomized to either a high-intensity or a low-intensity intervention group. The multidomain intervention comprises a combination of 7 lifestyle components (physical activity, cognitive training, cardiovascular risk factor management, nutritional counseling, sleep counseling, stress management, and social activities) and 1 nutritional product (Souvenaid®) that could help maintain cognitive functioning. The high-intensity intervention group receives a personalized, supervised and hybrid intervention consisting of group meetings (on-site and online) and individual sessions guided by a trained lifestyle coach, and access to a digital intervention platform that provides custom-made training materials and selected lifestyle apps. The low-intensity intervention group receives bi-monthly online lifestyle-related health advice via the digital intervention platform. Primary outcome is 2-year change on a cognitive composite score covering processing speed, executive function, and memory.
Results: Within 17 months, participant recruitment has been successfully completed (N = 1210; mean age: 67.7 years (SD: 4.6); 64% female). Modifiable risk factors commonly present at baseline were physical inactivity (89%), low mental/cognitive activity (50%), low social engagement (39%), hypertension (39%) and high alcohol consumption (39%). The mean body mass index of participants was 28.3 (SD: 4.2) and the total serum cholesterol was 5.4 mmol/L (SD: 1.2).
Conclusions: Baseline lifestyle and clinical measurements showed successful recruitment of participants with sufficient potential for prevention. Results of FINGER-NL will provide further insight into the efficacy of a multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline in older adults.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (ID: NCT05256199)/2022-01-11.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cognitive impairment; Dementia; Intervention; Lifestyle; Multidomain; Prevention; Randomized controlled trial; Risk factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Research programs of WF have been funded by ZonMW, NWO, EU-JPND, EU-IHI, Alzheimer Nederland, Hersenstichting CardioVascular Onderzoek Nederland, Health ~ Holland, Topsector Life Sciences & Health, stichting Dioraphte, Gieskes-Strijbis fonds, stichting Equilibrio, Edwin Bouw fonds, Pasman stichting, stichting Alzheimer & Neuropsychiatrie Foundation, Philips, Biogen MA Inc, Novartis-NL, Life-MI, AVID, Roche BV, Fujifilm, Eisai, Combinostics. WF holds the Pasman chair. WF is recipient of ABOARD, which is a public–private partnership receiving funding from ZonMW (#73305095007) and Health ~ Holland, Topsector Life Sciences & Health (PPP-allowance; #LSHM20106). WF is recipient of TAP-dementia (
LB is an employee of Danone Research & Innovation.
No conflict of interest were reported by the other co-authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Body, Brain, Life for Cognitive Decline (BBL-CD): protocol for a multidomain dementia risk reduction randomized controlled trial for subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment.Clin Interv Aging. 2018 Nov 21;13:2397-2406. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S182046. eCollection 2018. Clin Interv Aging. 2018. PMID: 30538436 Free PMC article.
-
A digitally supported multimodal lifestyle program to promote brain health among older adults (the LETHE randomized controlled feasibility trial): study design, progress, and first results.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Nov 21;16(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01615-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39574193 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
GOIZ ZAINDU study: a FINGER-like multidomain lifestyle intervention feasibility randomized trial to prevent dementia in Southern Europe.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Feb 27;16(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01393-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38413990 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-Domain Interventions for Dementia Prevention - A Systematic Review.J Nutr Health Aging. 2023;27(12):1271-1280. doi: 10.1007/s12603-023-2046-2. J Nutr Health Aging. 2023. PMID: 38151879
-
Face-to-Face and Digital Multidomain Lifestyle Interventions to Enhance Cognitive Reserve and Reduce Risk of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias: A Review of Completed and Prospective Studies.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 19;11(9):2258. doi: 10.3390/nu11092258. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31546966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of human concurrent aerobic and resistance training on cognitive health: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025 Jan-Mar;25(1):100559. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2025.100559. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40226294 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of interventions targeting modifiable factors for dementia risk reduction.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jun 23;20(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00845-w. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40551205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of targeted lifestyle interventions on brain function in young and middle-aged patients with hypertension: A retrospective cohort analysis.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Dec;40(11):2588-2593. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.11.10304. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39634900 Free PMC article.
-
CITA GO-ON study. A community based multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline. Protocol design and recruitment process.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Jun 16;17:1539711. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1539711. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40589624 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of efficiency and effectiveness of different recruitment strategies for the FINGER-NL multidomain lifestyle intervention trial via the Dutch Brain Research Registry.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025 Jan 9;11(1):e70017. doi: 10.1002/trc2.70017. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025. PMID: 39790861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on the public health response to dementia. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 17611/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical