MicroRNA-98: the multifaceted regulator in human cancer progression and therapy
- PMID: 38872210
- PMCID: PMC11177407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03386-2
MicroRNA-98: the multifaceted regulator in human cancer progression and therapy
Abstract
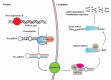
MicroRNA-98 (miR-98) stands as an important molecule in the intricate landscape of oncology. As a subset of microRNAs, these small non-coding RNAs have accompanied a new era in cancer research, underpinning their significant roles in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and therapeutic interventions. This review provides a comprehensive insight into the biogenesis, molecular properties, and physiological undertakings of miR-98, highlighting its double-edged role in cancer progression-acting both as a tumor promoter and suppressor. Intriguingly, miR-98 has profound implications for various aspects of cancer progression, modulating key cellular functions, including proliferation, apoptosis, and the cell cycle. Given its expression patterns, the potential of miR-98 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker, especially in liquid biopsies and tumor tissues, is explored, emphasizing the hurdles in translating these findings clinically. The review concludes by evaluating therapeutic avenues to modulate miR-98 expression, addressing the challenges in therapy resistance, and assessing the efficacy of miR-98 interventions. In conclusion, while miR-98's involvement in cancer showcases promising diagnostic and therapeutic avenues, future research should pivot towards understanding its role in tumor-stroma interactions, immune modulation, and metabolic regulation, thereby unlocking novel strategies for cancer management.
Keywords: MicroRNA-98; And biomarkers; Human cancers; Oncogenic; Tumor-suppressive.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The microRNA-202 as a Diagnostic Biomarker and a Potential Tumor Suppressor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 24;23(11):5870. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115870. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of miR-192 in cancer: a biomarker and therapeutic target.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Mar 14;25(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03666-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40087755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of miR-145 in gastrointestinal cancers: A new paradigm.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Oct;166:115264. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115264. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37619484 Review.
-
miRNA and cancer; computational and experimental approaches.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(5):429. doi: 10.2174/138920101505140828161335. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25189575
-
Unraveling the Multifaceted Role of the miR-17-92 Cluster in Colorectal Cancer: From Mechanisms to Biomarker Potential.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 28;46(3):1832-1850. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030120. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Oncogenic Pathways in Breast and Gynaecological Cancers.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Aug 6;11(4):61. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11040061. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40863727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro-Epigenetic Markers in Viral Genome: SARS-CoV-2 Infection Impact on Host Cell MicroRNA Landscape.Maedica (Bucur). 2024 Dec;19(4):842-847. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2024.19.4.842. Maedica (Bucur). 2024. PMID: 39974441 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis and noncoding RNAs: exploring mechanisms in lung cancer treatment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 26;13:1522873. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1522873. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40078365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehension of PTEN-Regulated MicroRNA Profiling in Oral Premalignant Lesions: A Critical Link to Early Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):e82343. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82343. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40385769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pilot Study on the Analysis of Circulating miRNA Upregulation in Laryngeal Cancer.Diseases. 2025 Mar 30;13(4):101. doi: 10.3390/diseases13040101. Diseases. 2025. PMID: 40277812 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

