ALKBH5 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression and susceptibility to anti-PD-L1 therapy by modulating interactions between tumor and macrophages
- PMID: 38872221
- PMCID: PMC11177518
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03073-0
ALKBH5 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression and susceptibility to anti-PD-L1 therapy by modulating interactions between tumor and macrophages
Abstract
Background: Understanding the mechanisms that mediate the interaction between tumor and immune cells may provide therapeutic benefit to patients with cancer. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethylase, ALKBH5 (alkB homolog 5), is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer. However, its role in the tumor microenvironment is unknown.
Methods: Datasets and tissue samples were used to determine the relationship between ALKBH5 expression and immunotherapy efficacy. Bioinformatic analysis, colorimetric assay to determine m6A RNA methylation, dual luciferase reporter assay, RNA/m6A-modified RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA stability assay, and RNA sequencing were used to investigate the regulatory mechanism of ALKBH5 in non-small cell lung cancer. In vitro and in vivo assays were performed to determine the contribution of ALKBH5 to the development of non-small cell lung cancer.
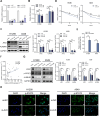
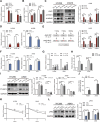
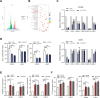
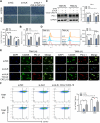
Results: ALKBH5 was upregulated in primary non-small cell lung cancer tissues. ALKBH5 was positively correlated with programmed death-ligand 1 expression and macrophage infiltration and was associated with immunotherapy response. JAK2 was identified as a target of ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification, which activates the JAK2/p-STAT3 pathway to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression. ALKBH5 was found to recruit programmed death-ligand 1-positive tumor-associated macrophages and promote M2 macrophage polarization by inducing the secretion of CCL2 and CXCL10. ALKBH5 and tumor-associated macrophage-secreted IL-6 showed a synergistic effect to activate the JAK2/p-STAT3 pathway in cancer cells.
Conclusions: ALKBH5 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by regulating cancer and tumor-associated macrophage behavior through the JAK2/p-STAT3 pathway and the expression of CCL2 and CXCL10, respectively. These findings suggest that targeting ALKBH5 is a promising strategy of enhancing the anti-tumor immune response in patients with NSCLC and that identifying ALKBH5 status could facilitate prediction of clinical response to anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy.
Keywords: ALKBH5; JAK2/p-STAT3 pathway; N6-methyladenosine demethylase; Non-small cell lung cancer; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-associated macrophage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82370096/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82172728/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BE2019719/Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program
- 2023JCYJZD080/Science and Technology Innovation Research Project of Jinling Hospital
- 22LCYY-LH3/Science and Technology Innovation Research Project of Jinling Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

