The heart rate response to the 6-min walk test in atrial fibrillation patients with or without beta-blockers: Referring to patients with sinus rhythm
- PMID: 38872457
- PMCID: PMC11176575
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.13128
The heart rate response to the 6-min walk test in atrial fibrillation patients with or without beta-blockers: Referring to patients with sinus rhythm
Abstract
Background: The aim was to evaluate the effect of beta-blockers (BB) on the response of heart rate (HR) to 6-min walk test (6MWT) in atrial fibrillation (AF) and whether the AF patients treated with BB have a similar HR response to 6MWT as the AF and sinus rhythm (SR) patients without BB treatment at the same resting HR level.
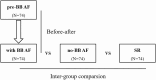
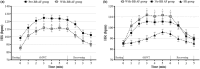
Methods: The before-after study involving 74 AF patients was to evaluate the effect of BB treatment (pre-BB and with BB). The comparison study included 74 BB-treated AF patients (with BB), 74 matched AF patients without BB (no BB), and 74 SR patients. The percentage increase amplitude of HR (HR-PIA) in 6MWT was calculated: [(the exercise HR - the resting HR)/(the resting HR)] × 100%.
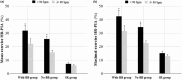
Results: The before-after study showed that BB treatment decreased the resting and mean exercise HR (98.6 ± 15.2 vs. 85.5 ± 11.2 bpm and 121.3 ± 17.3 vs. 109.0 ± 16.7 bpm) during 6MWT. The comparison study demonstrated that against the SR, the AF with BB and no BB groups have higher mean exercise HR-PIA (28.2 ± 17.1% and 22.0 ± 9.6%, vs. 6.9 ± 3.7%) when their resting HR is similar. Moreover, the mean exercise HR-PIA was also significantly higher in the with BB group than in the no BB group.
Conclusion: In AF patients with relatively higher resting HR, BB treatment could decrease the resting and exercise HR during 6MWT. However, BB treatment could not effectively attenuate the exercise HR rise as compared with AF without BB treatment, even with similar resting HR levels.
Keywords: 6‐min walk test; atrial fibrillation; beta‐blockers; exercise; heart rate.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in Heart Rate Response and Recovery After 6-Minute Walk Test Between Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and in Sinus Rhythm.Am J Cardiol. 2018 Aug 15;122(4):592-596. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.04.048. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Am J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29958713
-
Prognostic Significance of Resting Heart Rate and Use of β-Blockers in Atrial Fibrillation and Sinus Rhythm in Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: Findings From the Swedish Heart Failure Registry.Circ Heart Fail. 2015 Sep;8(5):871-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002285. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Circ Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 26243796
-
Prognostic impact of heart rate in elderly with systolic heart failure and concomitant atrial fibrillation.Scand Cardiovasc J. 2017 Aug;51(4):190-196. doi: 10.1080/14017431.2017.1314549. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2017. PMID: 28393567
-
Heart Rate and Rhythm and the Benefit of Beta-Blockers in Patients With Heart Failure.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Jun 20;69(24):2885-2896. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 30. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28467883 Review.
-
Pharmacologic management of atrial fibrillation: current therapeutic strategies.Am Heart J. 2001 Feb;141(2 Suppl):S15-21. doi: 10.1067/mhj.2001.109952. Am Heart J. 2001. PMID: 11174354 Review.
References
-
- Aihara, K. , Kato, Y. , Suzuki, S. , Arita, T. , Yagi, N. , Semba, H. , Kano, H. , Matsuno, S. , Otsuka, T. , Uejima, T. , Oikawa, Y. , Kunihara, T. , Yajima, J. , & Yamashita, T. (2018). Prognostic value of the heart rate profile during exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 25(15), 1634–1641. 10.1177/2047487318797398 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atwood, J. E. , Sullivan, M. , Forbes, S. , Myers, J. , Pewen, W. , Olson, H. G. , & Froelicher, V. F. (1987). Effect of beta‐adrenergic blockade on exercise performance in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 10(2), 314–320. 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80013-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corino, V. D. , Sandberg, F. , Platonov, P. G. , Mainardi, L. T. , Ulimoen, S. R. , Enger, S. , Tveit, A. , & Sörnmo, L. (2014). Non‐invasive evaluation of the effect of metoprolol on the atrioventricular node during permanent atrial fibrillation. Europace, 16, iv129–iv134. 10.1093/europace/euu246 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Farshi, R. , Kistner, D. , Sarma, J. S. , Longmate, J. A. , & Singh, B. N. (1999). Ventricular rate control in chronic atrial fibrillation during daily activity and programmed exercise: A crossover open‐label study of five drug regimens. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 33(2), 304–310. 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00561-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

