Mitochondrial membrane synthesis, remodelling and cellular trafficking
- PMID: 38872485
- PMCID: PMC11730691
- DOI: 10.1002/jimd.12766
Mitochondrial membrane synthesis, remodelling and cellular trafficking
Abstract
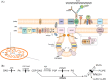
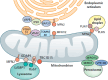
Mitochondria are dynamic cellular organelles with complex roles in metabolism and signalling. Primary mitochondrial disorders are a group of approximately 400 monogenic disorders arising from pathogenic genetic variants impacting mitochondrial structure, ultrastructure and/or function. Amongst these disorders, defects of complex lipid biosynthesis, especially of the unique mitochondrial membrane lipid cardiolipin, and membrane biology are an emerging group characterised by clinical heterogeneity, but with recurrent features including cardiomyopathy, encephalopathy, neurodegeneration, neuropathy and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria. This review discusses lipid synthesis in the mitochondrial membrane, the mitochondrial contact site and cristae organising system (MICOS), mitochondrial dynamics and trafficking, and the disorders associated with defects of each of these processes. We highlight overlapping functions of proteins involved in lipid biosynthesis and protein import into the mitochondria, pointing to an overarching coordination and synchronisation of mitochondrial functions. This review also focuses on membrane interactions between mitochondria and other organelles, namely the endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisomes, lysosomes and lipid droplets. We signpost disorders of these membrane interactions that may explain the observation of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction in heterogeneous pathological processes. Disruption of these organellar interactions ultimately impairs cellular homeostasis and organismal health, highlighting the central role of mitochondria in human health and disease.
Keywords: MAM; MERC; MICOS; cardiolipin; cell trafficking; mitochondrial lipid biosynthesis; organellar crosstalk; primary mitochondrial disease.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of SSIEM.
Conflict of interest statement
Martina Messina declares no competing interests. Frederic Maxime Vaz declares no competing interests. Shamima Rahman declares that she is an editor‐in‐chief of the Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease and has provided consultancy on primary mitochondrial diseases to pharmaceutical companies as listed in the IJCME conflict of interest form.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

