Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy in a Patient With Achalasia and Isolated Situs Inversus of the Liver
- PMID: 38872663
- PMCID: PMC11168899
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60229
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy in a Patient With Achalasia and Isolated Situs Inversus of the Liver
Abstract
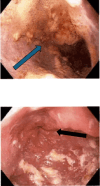
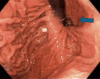
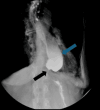
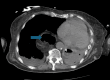
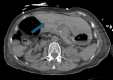
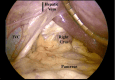
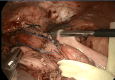
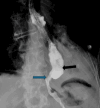
Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder characterized by incomplete lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxation, increased LES tone, and absent peristalsis in the esophagus. Management of achalasia includes pneumatic dilation (PD), Botulinum toxin A (BTA) injections to LES, per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), and a laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM). Situs inversus is a rare congenital condition in which the abdominal and thoracic organs are located in a mirror image of the normal position in the sagittal plane. We herein present a case of a patient with Type II achalasia who underwent an LHM and toupet fundoplication in the setting of an isolated laterality malposition of the liver on the left side of the abdomen. Single organ congenital lateralization defects are extremely rare with literature describing few case reports and case series. A much rarer condition is isolated organ situs inversus. In the foregut, most reports of isolated situs inversus are limited to isolated gastric situs inversus, dextrogastria. Most isolated liver malposition has described situs ambiguous, at the midline, usually associated with polysplenia. Our patient had the normal position of the foregut structures, including the stomach, spleen, pancreas, and duodenum, except for the isolated situs inversus of the liver. Because of the unusual anatomy, performing an LHM was quite challenging. Our workup approach and intraoperative considerations are described. By displacing the larger left lobe of the liver, we were able to safely complete a standard heller myotomy with adequate length and distally across the gastroesophageal junction. Our patient had an uncomplicated post-operative course, and at follow-up has continued to show improvements in her dysphagia and her quality of life.
Keywords: abdominal situs inversus; dextrohepatica; esophageal achalasia; esophagus; foregut; heller myotomy; isolated situs; minimally invasive; minimally invasive laparoscopy; visceral situs malposition.
Copyright © 2024, Prange et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Achalasia: incidence, prevalence and survival. A population-based study. Sadowski DC, Ackah F, Jiang B, Svenson LW. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22:256–261. - PubMed
-
- AGA technical review on the clinical use of esophageal manometry. Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:209–224. - PubMed
-
- Achalasia: a systematic review. Pandolfino JE, Gawron AJ. J Am Med Assoc. 2015;313:1841–1852. - PubMed
-
- Review article: the management of achalasia - a comparison of different treatment modalities. Lake JM, Wong RK. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:909–918. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
