Aspirin eugenol ester affects ileal barrier function, inflammatory response and microbiota in broilers under lipopolysaccharide-induced immune stress conditions
- PMID: 38872795
- PMCID: PMC11169880
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1401909
Aspirin eugenol ester affects ileal barrier function, inflammatory response and microbiota in broilers under lipopolysaccharide-induced immune stress conditions
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of aspirin eugenol ester (AEE) on ileal immune function in broilers under lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immune stress.
Methods: Two hundred and forty one-day-old male Arbor Acres chicks were randomly divided into four groups (saline, LPS, saline + AEE and LPS + AEE) with six replicates of ten broilers each. The saline group and LPS group were fed the normal diet, while the other two groups received normal diet plus 0.1 g/kg AEE. Broilers in the LPS and LPS + AEE groups were injected intraperitoneally with 0.5 mg/kg B.W LPS in saline for seven consecutive days beginning at 14 days of age, while broilers in the saline and saline + AEE groups were injected with saline only.
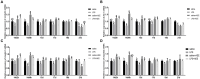
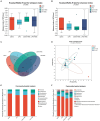
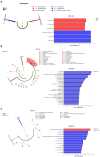
Results: The results showed that AEE improved the ileal morphology and increased the ratio of villus height to crypt depth of immune-stressed broilers. LPS-induced immune stress significantly reduced the expression of the genes for the tight junction proteins occludin, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), claudin-1 and claudin-2, in the ileum, while AEE significantly up-regulated the expression of these genes. Compared with the saline group, the LPS-treated chickens showed significantly increased mRNA expression of the inflammatory factors tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthesase-1 (mPGES-1) in the ileum, while they were significantly decreased by AEE supplementation. In addition, analysis of the ileal bacterial composition showed that compared with saline and LPS + AEE groups, the proportion of Firmicutes and Lactobacillus in the LPS group was lower, while the proportion of Proteobacteria and Escherichia-Shigella was higher. Similarly, Line Discriminant Analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) analysis showed that compared with the LPS group, Brevibacillus was dominant in the saline group, while the LPS + AEE group was rich in Rhizobium, Lachnoclostridium, Ruminococcaceae, Faecalibacterium, Negativibacillus, Oscillospiraceae, and Flavonifractor.
Conclusion: These results indicate that dietary supplementation with 0.1 g/kg AEE could protect the intestinal health by improving the intestinal villus morphology, enhancing the expression of tight junction genes and alleviating inflammation to resist the immune stress caused by LPS stimulation in broilers, and the mechanism may involve COX-2-related signal transduction and improved intestinal microbiota composition.
Keywords: aspirin eugenol ester; broiler; ileal microbiota; immune stress; intestinal barrier function.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Bai, Zhen, Hu, Zhang, Zhong, Zhang, Ito, Zhang, Yang, Li and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary chlorogenic acid on intestinal barrier function and the inflammatory response in broilers during lipopolysaccharide-induced immune stress.Poult Sci. 2023 May;102(5):102623. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102623. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36972676 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary l-threonine supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and intestinal barrier damage of broiler chickens at an early age.Br J Nutr. 2018 Jun;119(11):1254-1262. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518000740. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29770758 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dietary aspirin eugenol ester on the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal inflammation, and cecal microbiota of broilers under high stocking density.Poult Sci. 2024 Jul;103(7):103825. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103825. Epub 2024 May 11. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38772090 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary supplementation with aspirin eugenol ester on performance and ileum health in broilers under high stocking density stress conditions.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 7;12:1638245. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1638245. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40693110 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary leonurine hydrochloride supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide challenge-induced intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction by inhibiting the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway in broilers.J Anim Sci. 2019 Apr 3;97(4):1679-1692. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz078. J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 30789669 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Selenium-enriched Lactobacillus coryniformis H8 alleviates LPS-induced jejunal injury in chicks by modulating antioxidant activity, inflammation, selenoprotein genes, and gut microbiota.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug 13;104(11):105675. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105675. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40840291 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Inflammation in Wenchang Chicken by Inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 2;12(3):225. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030225. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40266904 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorogenic acid alters ileal microbiota and metabolites in broiler chickens under immune stress.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0331224. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03312-24. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40503877 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of berberine on LPS-induced intestinal epithelial injury and m6A methylation in broilers.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug 12;104(11):105677. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105677. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40829428 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

