Research on drought stress in Medicago sativa L. from 1998 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38872890
- PMCID: PMC11169798
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1406256
Research on drought stress in Medicago sativa L. from 1998 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
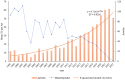
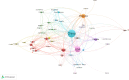
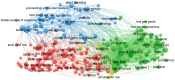
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is one of the most important forage crops in the world. Drought is recognized as a major challenge limiting alfalfa production and threatening food security. Although some literature reviews have been conducted in this area, bibliometric reviews based on large amounts of published data are still lacking. In this paper, a bibliometric analysis of alfalfa drought stress from 1998-2023 was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection database in order to assess global trends in alfalfa drought stress research and to provide new directions for future research. The results showed that the annual publication output maintained an increase in most years, with China and the United States contributing significantly to the field. Most of the journals published are specialized journals in botany, environmental science, soil science and crop science, as well as related agribusiness journals. "plant growth" and "yield" were the most frequently used keywords, reflecting the important purpose of research in this field. And two main research directions were identified: research on drought response mechanism of alfalfa and exploration of drought-resistant technology. In addition, physiological, biochemical, and molecular responses of drought tolerance and high yield in alfalfa, transgenics, and microbial fertilizer research have been hot research topics in recent years and may continue in the future. The ultimate goal of this paper is to provide a foundational reference for future research on alfalfa's drought resistance and yield optimization mechanisms, thereby enhancing the crop's application in agricultural production.
Keywords: alfalfa; bibliometrics; drought tolerance; research trends; response mechanism; yield.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Li, Gao, Wang, Wang, Huang, Zhang, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
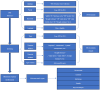
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Alfalfa Response to Abiotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;14(3):487. doi: 10.3390/plants14030487. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends and Directions in Oats Research under Drought and Salt Stresses: A Bibliometric Analysis (1993-2023).Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;13(14):1902. doi: 10.3390/plants13141902. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thriving in a salty future: morpho-anatomical, physiological and molecular adaptations to salt stress in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and other crops.Ann Bot. 2024 Dec 31;134(7):1113-1130. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcae152. Ann Bot. 2024. PMID: 39215647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of the Aux/IAA (auxin/indole-3-acetic acid) gene family in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and the potential functions under drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 18;25(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10313-2. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38637768 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of Different Medicago sativa L. Varieties Under Drought Stress.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;14(5):639. doi: 10.3390/plants14050639. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40094522 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of expression patterns of the ABC1K gene family members in Medicago sativa.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Nov 25;15:1486525. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1486525. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39654960 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in basic biology of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): a comprehensive overview.Hortic Res. 2025 Mar 10;12(7):uhaf081. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhaf081. eCollection 2025 Jul. Hortic Res. 2025. PMID: 40343348 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Alfalfa Response to Abiotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;14(3):487. doi: 10.3390/plants14030487. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response of seed germination and seedling growth of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) to drought, salinity, and pH in Karst regions.Sci Rep. 2025 May 15;15(1):16874. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01539-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40374789 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and Directions in Oats Research under Drought and Salt Stresses: A Bibliometric Analysis (1993-2023).Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;13(14):1902. doi: 10.3390/plants13141902. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anjum S. A., Ashraf U., Zohaib A., Tanveer M., Naeem M., Ali I., et al. . (2017). Growth and developmental responses of crop plants under drought stress: a review. Zemdirbyste 104, 267–276. doi: 10.13080/z-a.2017.104.034 - DOI
-
- Annicchiarico P. (2007). Lucerne shoot and root traits associated with adaptation to favourable or drought-stress environments and to contrasting soil types. Field Crop Res. 102, 51–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2007.01.005 - DOI
-
- Annicchiarico P., Barrett B., Brummer E. C., Julier B., Marshall A. H. (2014). Achievements and challenges in improving temperate perennial forage legumes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 34, 327–380. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2014.898462 - DOI
-
- Annicchiarico P., Pecetti L., Tava A. (2012). Physiological and morphological traits associated with adaptation of lucerne (Medicago sativa) to severely drought-stressed and to irrigated environments. Ann. Appl. Biol. 162, 27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2012.00576.x - DOI
-
- Anower M. R., Boe A., Auger D., Mott I. W., Peel M. D., Xu L., et al. . (2015). Comparative drought response in eleven diverse alfalfa accessions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 203, 1–13. doi: 10.1111/jac.12156 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

