Integrating GC-MS and comparative transcriptome analysis reveals that TsERF66 promotes the biosynthesis of caryophyllene in Toona sinensis tender leaves
- PMID: 38872893
- PMCID: PMC11171135
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1378418
Integrating GC-MS and comparative transcriptome analysis reveals that TsERF66 promotes the biosynthesis of caryophyllene in Toona sinensis tender leaves
Abstract
Introduction: The strong aromatic characteristics of the tender leaves of Toona sinensis determine their quality and economic value.
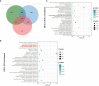
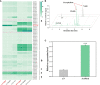
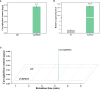
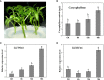
Methods and results: Here, GC-MS analysis revealed that caryophyllene is a key volatile compound in the tender leaves of two different T. sinensis varieties, however, the transcriptional mechanisms controlling its gene expression are unknown. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed significant enrichment of terpenoid synthesis pathway genes, suggesting that the regulation of terpenoid synthesis-related gene expression is an important factor leading to differences in aroma between the two varieties. Further analysis of expression levels and genetic evolution revealed that TsTPS18 is a caryophyllene synthase, which was confirmed by transient overexpression in T. sinensis and Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Furthermore, we screened an AP2/ERF transcriptional factor ERF-IX member, TsERF66, for the potential regulation of caryophyllene synthesis. The TsERF66 had a similar expression trend to that of TsTPS18 and was highly expressed in high-aroma varieties and tender leaves. Exogenous spraying of MeJA also induced the expression of TsERF66 and TsTPS18 and promoted the biosynthesis of caryophyllene. Transient overexpression of TsERF66 in T. sinensis significantly promoted TsTPS18 expression and caryophyllene biosynthesis.
Discussion: Our results showed that TsERF66 promoted the expression of TsTPS18 and the biosynthesis of caryophyllene in T. sinensis leaves, providing a strategy for improving the aroma of tender leaves.
Keywords: AP2/ERF; Terpene synthase (TPS); Toona sinensis; caryophyllene; transient overexpression.
Copyright © 2024 Dai, Wang, Yin, Han, Fan, Wei, Lin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential gene expression and metabolic pathways in Toona sinensis: Influence on colour and aroma.Physiol Plant. 2025 Mar-Apr;177(2):e70146. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70146. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40069569 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and volatilomic profiles to explore the potential mechanism of aroma formation in Toona sinensis.Food Res Int. 2023 Mar;165:112452. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112452. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36869447
-
Integration of transcriptome, volatile and non-volatile metabolite profile reveals characteristic aroma formation in Toona sinensis.Food Chem. 2024 Mar 15;436:137788. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137788. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 37866100
-
Biosynthesis and the Transcriptional Regulation of Terpenoids in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 8;24(8):6937. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086937. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Uses, Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of the Toona sinensis Plant.Molecules. 2024 Feb 4;29(3):718. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030718. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two Terpene Synthases Are Involved in Multiple Sesquiterpene Biosynthesis in the Woody Vegetable, Toona sinensis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 13;26(4):1578. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041578. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrož M., Boušová I., Skarka A., Hanušová V., Králová V., Matoušková P., et al. . (2015). The influence of sesquiterpenes from Myrica rubra on the antiproliferative and pro-oxidative effects of doxorubicin and its accumulation in cancer cells. Molecules 20, 15343–15358. doi: 10.3390/molecules200815343 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

