Understanding Fibrous Tissue in the Effective Healing of Rotator Cuff Injury
- PMID: 38872898
- PMCID: PMC11174978
- DOI: 10.26502/jsr.10020363
Understanding Fibrous Tissue in the Effective Healing of Rotator Cuff Injury
Abstract
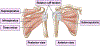
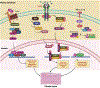
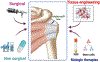
The rotator cuff is a crucial group of muscles and tendons in the shoulder complex that plays a significant role in the stabilization of the glenohumeral joint and enabling a wide range of motion. Rotator cuff tendon tears can occur due to sudden injuries or degenerative processes that develop gradually over time, whether they are partial or full thickness. These injuries are common causes of shoulder pain and functional impairment, and their complex nature highlights the essential role of the rotator cuff in shoulder function. Scar formation is a crucial aspect of the healing process initiated following a rotator cuff tendon tear, but excessive fibrous tissue development can potentially lead to stiffness, discomfort, and movement limitations. Age is a critical risk factor, with the prevalence of these tears increasing among older individuals. This comprehensive review aims to delve deeper into the anatomy and injury mechanisms of the rotator cuff. Furthermore, it will inspect the signaling pathways involved in fibrous tissue development, evaluate the various factors affecting the healing environment, and discuss proactive measures aimed at reducing excessive fibrous tissue formation. Lastly, this review identifed gaps within existing knowledge to advance methods for better management of rotator cuff tendon injuries.
Keywords: Collagen; Fibrous tissue; Pathways; Rotator cuff; Tendons.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests. Both authors have read the manuscript and declare no conflict of interest. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
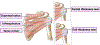
Similar articles
-
Isolated Bioinductive Arthroscopic Repair of Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Using a Resorbable Collagen Implant.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2022 Jan 25;12(1):e21.00008. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.21.00008. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2022. PMID: 35685236 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Radiologic Outcomes of Degenerative Versus Traumatic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Involving the Supraspinatus Tendon.Am J Sports Med. 2024 Feb;52(2):441-450. doi: 10.1177/03635465231219253. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Am J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 38259113 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical analysis of articular-sided partial-thickness rotator cuff tear and repair.Am J Sports Med. 2015 Feb;43(2):439-46. doi: 10.1177/0363546514560156. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Am J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25512665
-
Epidemiology, natural history, and indications for treatment of rotator cuff tears.Clin Sports Med. 2012 Oct;31(4):589-604. doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Clin Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 23040548 Review.
-
Rotator Cuff Injuries in Tennis Players.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020 Dec;13(6):734-747. doi: 10.1007/s12178-020-09675-3. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020. PMID: 32827301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychological Treatment in the Management of Pain following Musculoskeletal Injury.J Orthop Sports Med. 2025;7(1):162-168. doi: 10.26502/josm.511500191. Epub 2025 Mar 31. J Orthop Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40297561 Free PMC article.
-
Rotator Cuff Injury: Pathogenesis, Biomechanics, and Repair.J Orthop Sports Med. 2024;6(4):231-248. doi: 10.26502/josm.511500167. Epub 2024 Oct 22. J Orthop Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39574962 Free PMC article.
-
Biologically Enhanced Patch in the Healing and Mechanical Stability of Rotator Cuff Tears.J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024;7(3):379-387. doi: 10.26502/jbb.2642-91280161. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39364329 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Medicinal Plants with Allopathic Medicine in Musculoskeletal Diseases.Int J Plant Anim Environ Sci. 2024;14(4):104-129. doi: 10.26502/ijpaes.4490170. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Int J Plant Anim Environ Sci. 2024. PMID: 39866300 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between SLAP Lesions and Shoulder Joint Capsule Thickness: An MR Arthrographic Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 16;60(8):1332. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081332. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maruvada SA, Madrazo IM, Anatomy V. Rotator Cuff in: StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) (2023).
-
- Jeno SH, Munjal A, Schindler GS. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Arm Supraspinatus Muscle, in: StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) (2023). - PubMed
-
- Waldman SD. 34 - Infraspinatus Tendon Injection, in: Waldman SD (Ed.), Atlas Pain Manag. Inject. Tech. 5th edtn., Elsevier, 12 (2023): 126–129.
-
- Chambers MM, Khan A, Namdari S, et al. Minor Muscle Atrophy: Anatomy, Patterns, and Clinical Manifestations. JBJS Rev 10 (2022) e22.00130. - PubMed
-
- Waldman SD. 35 - Subscapularis Tendon Injection, in: Waldman SD (Ed.), Atlas Pain Manag. Inject. Tech. Fifth Ed., Elsevier; 12 (2023): 130–132.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
