iSIM: instant similarity
- PMID: 38873032
- PMCID: PMC11167700
- DOI: 10.1039/d4dd00041b
iSIM: instant similarity
Abstract
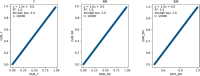
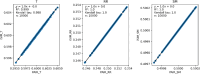
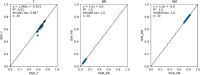
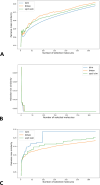
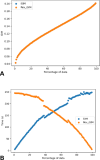
The quantification of molecular similarity has been present since the beginning of cheminformatics. Although several similarity indices and molecular representations have been reported, all of them ultimately reduce to the calculation of molecular similarities of only two objects at a time. Hence, to obtain the average similarity of a set of molecules, all the pairwise comparisons need to be computed, which demands a quadratic scaling in the number of computational resources. Here we propose an exact alternative to this problem: iSIM (instant similarity). iSIM performs comparisons of multiple molecules at the same time and yields the same value as the average pairwise comparisons of molecules represented by binary fingerprints and real-value descriptors. In this work, we introduce the mathematical framework and several applications of iSIM in chemical sampling, visualization, diversity selection, and clustering.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extended similarity indices: the benefits of comparing more than two objects simultaneously. Part 1: Theory and characteristics†.J Cheminform. 2021 Apr 23;13(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13321-021-00505-3. J Cheminform. 2021. PMID: 33892802 Free PMC article.
-
Extended similarity indices: the benefits of comparing more than two objects simultaneously. Part 2: speed, consistency, diversity selection.J Cheminform. 2021 Apr 23;13(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13321-021-00504-4. J Cheminform. 2021. PMID: 33892799 Free PMC article.
-
iCliff Taylor's version: Robust and Efficient Activity Cliff Determination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.09.642269. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.09.642269. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5801-5810. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00506. PMID: 40161667 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Molecular descriptors in chemoinformatics, computational combinatorial chemistry, and virtual screening.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2000 Oct;3(5):363-72. doi: 10.2174/1386207003331454. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2000. PMID: 11032954 Review.
-
Improving Molecular Contrastive Learning via Faulty Negative Mitigation and Decomposed Fragment Contrast.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Jun 13;62(11):2713-2725. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00495. Epub 2022 May 31. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 35638560 Review.
Cited by
-
Scaling k-Means for Multi-Million Frames: A Stratified NANI Approach for Large-Scale MD Simulations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 18:2025.06.15.659780. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.15.659780. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666979 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Extended Quality (eQual): Radial threshold clustering based on n-ary similarity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 5:2024.12.05.627001. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.05.627001. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 May 26;65(10):5062-5070. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c02341. PMID: 39677679 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CADENCE: Clustering Algorithm - Density-based Exploration and Novelty Clustering with Efficiency.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 28:2025.02.24.639863. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.24.639863. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jul 14;65(13):6968-6975. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00392. PMID: 40060588 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SHINE: Deterministic Many-to-Many Clustering of Molecular Pathways.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 May 26;65(10):4775-4782. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00240. Epub 2025 May 6. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40326720 Free PMC article.
-
BitBIRCH Clustering Refinement Strategies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 24:2025.03.20.644337. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.20.644337. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5280-5288. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00627. PMID: 40196520 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Todeschini R. and Consonni V., Handbook of Molecular Descriptors, Wiley, 2000
-
- Jaccard P. New Phytol. 1912;11:37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1912.tb05611.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
