Altered gut microbe metabolites in patients with alcohol‑induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: An integrated omics analysis
- PMID: 38873043
- PMCID: PMC11170330
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12599
Altered gut microbe metabolites in patients with alcohol‑induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: An integrated omics analysis
Abstract
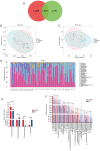
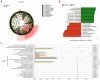
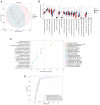
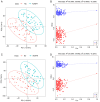
Excessive alcohol consumption is considered to be a major risk factor of alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (AONFH). The gut microbiota (GM) has been reported to aid in the regulation of human physiology and its composition can be altered by alcohol consumption. The aim of the present study was to improve the understanding of the GM and its metabolites in patients with AONFH. Metabolomic sequencing and 16S rDNA analysis of fecal samples were performed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to characterize the GM of patients with AONFH and healthy normal controls (NCs). Metagenomic sequencing of fecal samples was performed to identify whether GM changes on the species level were associated with the expression of gut bacteria genes or their associated functions in patients with AONFH. The abundance of 58 genera was found to differ between the NC group and the AONFH group. Specifically, Klebsiella, Holdemanella, Citrobacter and Lentilactobacillus were significantly more abundant in the AONFH group compared with those in the NC group. Metagenomic sequencing demonstrated that the majority of the bacterial species that exhibited significantly different abundance in patients with AONFH belonged to the genus Pseudomonas. Fecal metabolomic analysis demonstrated that several metabolites were present at significantly different concentrations in the AONFH group compared with those in the NC group. These metabolites were products of vitamin B6 metabolism, retinol metabolism, pentose and glucuronate interconversions and glycerophospholipid metabolism. In addition, these changes in metabolite levels were observed to be associated with the altered abundance of specific bacterial species, such as Basidiobolus, Mortierella, Phanerochaete and Ceratobasidium. According to the results of the present study, a comprehensive landscape of the GM and metabolites in patients with AONFH was revealed, suggesting the existence of interplay between the gut microbiome and metabolome in AONFH pathogenesis.
Keywords: alcohol; gut microbiota; metabolite; metagenomics; osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Copyright: © 2024 Yue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid metabolism analysis for peripheral blood in patients with alcohol-induced and steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jul 28;47(7):872-880. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210567. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36039583 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head induced by steroid and alcohol exposure is associated with intestinal flora alterations and metabolomic profiles.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 12;19(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04713-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38609952 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolite profiles of patients with Kashin-Beck disease, an endemic osteoarthritis in China.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 28;12(11):1015. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04322-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34711812 Free PMC article.
-
Less sclerotic microarchitecture pattern with increased bone resorption in glucocorticoid-associated osteonecrosis of femoral head as compared to alcohol-associated osteonecrosis of femoral head.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 8;14:1133674. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1133674. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36967755 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma lipidomics analysis reveals altered lipids signature in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Metabolomics. 2022 Feb 11;18(2):14. doi: 10.1007/s11306-022-01872-0. Metabolomics. 2022. PMID: 35147763
Cited by
-
The bibliometric and visualization analysis of alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: research trends and future directions (1998-2024).J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Aug 2;20(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06138-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40753253 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
