Common hematological and biochemical parameters for predicting urinary tract infections in geriatric patients with hip fractures
- PMID: 38873209
- PMCID: PMC11169829
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1333472
Common hematological and biochemical parameters for predicting urinary tract infections in geriatric patients with hip fractures
Abstract
Background: This study aims to discern the significance of common hematological and biochemical parameters for predicting urinary tract infections in geriatric patients with hip fractures.
Methods: Multivariable logistic regression and propensity score-matched analyses were conducted to calculate adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for UTIs. The abilities of these parameters to predict UTIs were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Dose-response relationships were assessed by categorizing hematological and biochemical parameters into quartiles. Subgroup analyses were further explored to investigate the relationship between these parameters and urinary tract infections.
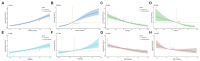
Results: Out of the 1,231 participants, 23.2% were diagnosed with UTIs. Hyperglycemia, hypoproteinemia and hyperglobulinemia were risk factors for UTIs in multivariate analysis. After propensity score matching, hyperglycemia (OR 2.14, 95% CI 1.50-3.05, p < 0.001), hypoproteinemia (OR 1.75, 95% CI 1.18-2.63, p = 0.006), and hyperglobulinemia (OR 1.38, 95% CI 0.97-1.97, p = 0.074) remained significantly associated with increased odds of urinary tract infections. ROC curve analyses showed moderate predictive accuracy of blood glucose, albumin and globulin for UTIs, with areas under the curves of 0.714, 0.633, and 0.596, respectively. Significant dose-response relationships were observed between these parameters and UTIs. The associations were consistent in subgroup analyses.
Conclusion: Blood glucose, albumin and globulin levels can facilitate early identification of geriatric hip fracture patients at high risk of UTIs. These easily obtainable hematological and biochemical parameters provide a practical clinical prediction tool for individualized UTI prevention in this population.
Keywords: geriatrics; hematological and biochemical parameters; hip fracture; predicting; urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2024 Tang, Ni, Yao, Wang, Li, Lv, Ding and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucose-albumin ratio (GAR) as a novel biomarker for predicting postoperative pneumonia (POP) in older adults with hip fractures.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 4;14(1):26637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60390-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39496632 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between admission hyperglycaemia and urinary tract infections in geriatric patients with hip fractures.Int Orthop. 2023 Oct;47(10):2591-2600. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05882-y. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Int Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37436524
-
Association between admission hyperglycemia and postoperative pneumonia in geriatric patients with hip fractures.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Sep 1;24(1):700. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06829-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37658378 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between admission hypoalbuminemia and postoperative urinary tract infections in elderly hip fracture patients.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Oct 14;18(1):774. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04274-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37838687 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Probiotics as Prophylaxis for Urinary Tract Infections in Premenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2021 Oct 17;13(10):e18843. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18843. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34671514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Common Hematologic Parameters and Novel Hematologic Ratios for Predicting Piroplasmosis Infection in Horses.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 20;15(10):1485. doi: 10.3390/ani15101485. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427362 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Blood Biochemical Parameters and Ratios in Piroplasmosis-Infected Horses in an Endemic Region.Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 5;12(7):643. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12070643. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711303 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

