Association between Life's Essential 8 and estimated pulse wave velocity among adults in the US: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2011-2018
- PMID: 38873301
- PMCID: PMC11169870
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1388424
Association between Life's Essential 8 and estimated pulse wave velocity among adults in the US: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2011-2018
Abstract
Background: Arterial stiffness, typically evaluated via estimated pulse wave velocity (ePWV), is believed to have a significant association with cardiovascular diseases. The objective of this study was to investigate the correlation between Life's Essential 8 (LE8), a newly revised metric of cardiovascular health, and ePWV among adult population in the United States.
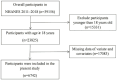
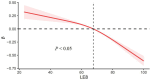
Methods: This research employed a cross-sectional methodology, drawing upon data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning from 2011 to 2018. To explore the relationship between LE8 and ePWV among adults in the US, both univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses were carried out. Additionally, the restricted cubic splines method was utilized to examine any non-linear correlation.
Results: The study comprised 6,742 participants with an average age of 48.30 ± 0.35 years. Among these, 3,236 were males, representing a weighted percentage of 48%. The population's weighted average LE8 score was 68.68 ± 0.37, while the average ePWV was 8.18 ± 0.04. An entirely adjusted model revealed a negative correlation between ePWV and LE8 scores [in the moderate LE8 group, coefficient - 0.17, 95% CI -0.28 to -0.06, p = 0.004; in the high LE8 group, coefficient - 0.44, 95% CI -0.56 to -0.32, p < 0.0001]. This negative correlation was consistent with the findings in demographic subgroup analysis, with the effect size being more pronounced among adults under the age of 60, and individuals without hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or diabetes.
Conclusion: Our study reveals a negative correlation between LE8 and ePWV in the adult population of the US, suggesting that LE8 could potentially serve as an indicative marker for evaluating the risk of vascular stiffness. This inverse relationship is markedly stronger in adults below 60 years and those without diagnosed vascular diseases. This implies that lifestyle upgrades and risk factor management could be especially advantageous in curbing arterial stiffness within these groups. These conclusions underscore the importance of primary prevention in mitigating the risk of vascular aging in a relatively healthy group, emphasizing the significance of early intervention and risk factor management in cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Life’s Essential 8; NHANES; cardiovascular health; ePWV; vascular aging.
Copyright © 2024 Fan, Yang, Ruan, Zhang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, et al. . Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association’s strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. (2010) 121:586–613. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192703, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Ning H, Labarthe D, Brewer L, Sharma G, Rosamond W, et al. . Status of cardiovascular health in US adults and children using the American Heart Association's new "Life's essential 8" metrics: prevalence estimates from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES), 2013 through 2018. Circulation. (2022) 146:822–35. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060911, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources