Endothelial Dysfunction Linked to Ventricular Dysfunction in Children With Sickle Cell Disease, a 3D Speckle Tracking Study
- PMID: 38873326
- PMCID: PMC11172668
- DOI: 10.37616/2212-5043.1369
Endothelial Dysfunction Linked to Ventricular Dysfunction in Children With Sickle Cell Disease, a 3D Speckle Tracking Study
Abstract
Background: Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is not a hematologic disease that occurs in isolation; it results in multi-organ complications. There is growing evidence of vascular stiffness as its underlying cause. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between endothelial stiffness and LV dysfunction in SCD patients and to explore its pathophysiology, particularly regarding the depletion of vasodilators such as Nitric Oxide (NO).
Methodology: 32 patients with established criteria for SCD and 40 healthy control subjects were selected for this case-control study. Comprehensive clinical assessment and assessment of endothelial function using Brachial Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) were performed, along with serum NO measurement, which was followed by diagnosis and echocardiographic assessment using 3D speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) and tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
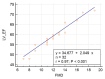
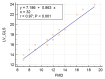
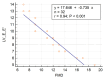
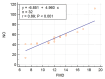
Results: Collected SCD cases showed echocardiographic features of Systo-diastolic dysfunction with reduced FMD compared to controls, denoting endothelial dysfunction in those patients. LDH showed a marked elevation, while serum NO showed a significant reduction in cases compared with controls. We also noted a positive correlation between FMD on the one hand and measures of ventricular dysfunction and level of serum NO on the other hand, the latter proving that reduction of NO is responsible for reduced endothelial function.
Conclusion: We present the first report to date to outline the role of vascular stiffness as measured by brachial FMD in the induction of left ventricular dysfunction in SCD. We recommend that more research be conducted regarding possible strategies to replenish serum NO stores to delay microvascular injury and, in turn, ventricular dysfunction in SCD.
Keywords: Flow-mediated dilation; Microvascular dysfunction; Myocardial injury; Nitric oxide; SCD; Speckle tracking.
© 2024 Saudi Heart Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors declare “no conflict of interest.”
Figures
References
-
- Zaidi GZ, Rosentsveyg JA, Fomani KF, Louie JP, Koenig SJ. Reversal of severe multiorgan failure associated with sickle cell crisis using plasma exchange: a case series. J Intensive Care Med [Internet] 2020 Feb 2;35(2):140–8. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0885066619874041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bawor M, Kesse-Adu R, Gardner K, Marino P, Howard J, Webb J. Prevalence of cardiac abnormalities in sickle cell disease identified using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Heart J [Internet] 2020 Nov 1;41(Supplement_2) Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/doi/10.1093/ehjci/ehaa946.102.... - DOI
-
- Antwi-Boasiako C, Campbell A. Low nitric oxide level is implicated in sickle cell disease and its complications in Ghana. Vasc Health Risk Manag [Internet] 2018 Sep;14:199–204. Available from: https://www.dovepress.com/low-nitric-oxide-level-is-implicated-in-sickle.... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azu CN, Kansal M, Jacob SA, Parikh D, Sachdev V, Patel AR, et al. Right ventricular strain analysis in a large cohort of patients with sickle cell disease. J Am Coll Cardiol [Internet] 2022;79(9):1671. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(22)02662-6. Available from: - DOI
-
- AbdelMassih AF, Salama KM, Ghobrial C, Haroun B, Rahman MA. Discrepancy in patterns of myocardial involvement in beta-thalassaemia vs. sickle cell anaemia. Acta Cardiol [Internet] 2020 Sep 2;75(5):442–9. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00015385.2019.1610836. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
