Mechanism of isorhynchophylline in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury based on proteomic technology
- PMID: 38873411
- PMCID: PMC11169627
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1397498
Mechanism of isorhynchophylline in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury based on proteomic technology
Abstract
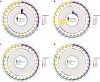
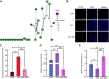
Isorhynchophylline (IRN), a tetracyclic indole alkaloid, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities against cardiovascular diseases and central nervous system disorders. Acute lung injury (ALI) is a manifestation of inflammation concentrated in the lungs and has a high incidence rate and mortality The purpose of this study is to explain the mechanism of IRN in the treatment of acute lung injury and to provide a new scheme for clinical treatment. The experimental mice were divided into three groups: CTRL, LPS, LPS+IRN. The mouse model of ALI was established by inhaling LPS solution through nose. After continuous administration of IRN solution for 7 days, the mice in LPS+IRN group were killed and the lung tissue was collected for detection. Proteomic (Data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD050432) results showed that 5727 proteins were detected in mouse lung tissues, and 16 proteins were screened out. IRN could reverse the trend of these differential proteins. In addition, IRN can act on integrin αM to reduce neutrophil recruitment and thereby produce anti-inflammatory effects and may suppress neutrophil migration through the leukocyte transendothelial migration pathway. TUNEL and RT-PCR experiments revealed that LPS-induced ALI in mice increases the apoptosis of lung tissues, damage to alveolar epithelial cells and levels of inflammatory factors. Treatment with IRN can repair tissues, improve lung tissue pathology and reduce lung inflammation.
Keywords: Nano-LC-MS/MS; RT-PCR; TUNEL; acute lung injury; isorhynchophylline; proteomic technology.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Xing, Qin, Zhang, Yang and Qiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Isorhynchophylline exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities in LPS-stimulated murine alveolar macrophages.Life Sci. 2019 Apr 15;223:137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.017. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30858121
-
Isorhynchophylline ameliorates paraquat-induced acute kidney injury by attenuating oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage via regulating toll-interacting expression.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 1;420:115521. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115521. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33838153
-
Inhibition of KLF6 reduces the inflammation and apoptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells in acute lung injury.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022 Sep 1;50(5):138-147. doi: 10.15586/aei.v50i5.632. eCollection 2022. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022. PMID: 36086974
-
Isorhynchophylline exerts anti-asthma effects in mice by inhibiting the proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells: The involvement of miR-200a-mediated FOXC1/NF-κB pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jan 22;521(4):1055-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.178. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31733831
-
Isorhynchophylline alleviates learning and memory impairments induced by aluminum chloride in mice.Chin Med. 2018 Jun 14;13:29. doi: 10.1186/s13020-018-0187-8. eCollection 2018. Chin Med. 2018. PMID: 29946349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai J., Hua Z. Z., Zhang C. R., Huang D, Zhang Q. H, Wang Y., et al. (2023). The effect of isoleucine on airway inflammation in asthmatic mice. Chin. Pharm. 34 (22), 2740–2744. 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2023.22.09 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

