Polygalae Radix: review of metabolites, pharmacological activities and toxicology
- PMID: 38873413
- PMCID: PMC11169621
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1420853
Polygalae Radix: review of metabolites, pharmacological activities and toxicology
Abstract
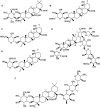
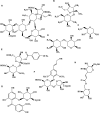
Polygalae Radix: is the dried root of Polygala tenuifolia Willd. or Polygala sibirica L., which has the effect of improving memory and cognitive function in traditional Chinese medicine. Modern pharmacological studies indicated that Polygalae Radix has rich pharmacological activities in vitro and in vivo, including protective effects on the nervous system, immune system, cardiovascular system and respiratory system, as well as antioxidant and antiepileptic pharmacological activities. Up to now, more than 160 metabolites from Polygalae Radix were identified, including triterpenoid saponins, xanthones, oligosaccharide esters and et al. The clinical practice of traditional Chinese medicine has proved that Polygalae Radix has a certain irritation to the throat, and a large or long-term use will stimulate the digestive tract, and the main toxic metabolite is saponins. Therefore, Polygalae Radix should be pr ocessed or used in combination with other Chinese herbal medicines to reduce the irritation to the throat and reduce gastrointestinal irritation. This article provides a review of the metabolites, pharmacological activity, and toxicology of Polygalae Radix. It also discusses the future research prospects and existing problems of Polygalae Radix, providing reference for further research on Polygalae Radix.
Keywords: Polygalae Radix; biological activity; immune system; metabolites; toxicology.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Wang and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
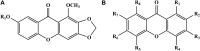
Similar articles
-
Polygalae Radix: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, and pharmacokinetics.Fitoterapia. 2020 Nov;147:104759. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104759. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Fitoterapia. 2020. PMID: 33069838 Review.
-
A review of the botany, metabolites, pharmacology, toxicity, industrial applications, and processing of Polygalae Radix: the "key medicine for nourishing life".Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1450733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1450733. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39359244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects and Mechanism of Radix Polygalae Against Neurological Diseases as Well as Effective Substance.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 17;12:688703. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.688703. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34975553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress on Polygalae Radix].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Nov;46(22):5744-5759. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210518.601. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34951162 Review. Chinese.
-
Illumination on "Reserving Phloem and Discarding Xylem" and Quality Evaluation of Radix polygalae by Determining Oligosaccharide Esters, Saponins, and Xanthones.Molecules. 2018 Apr 5;23(4):836. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040836. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29621185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen S., Lin L., Chen S., Yang D., Yang J., Xiao P. (2005). Quantitative determination of nine xanthones in polygala caudata and fingerprinting of polygala L. By HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 28, 2953–2963. 10.1080/10826070500274588 - DOI
-
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China (1987) Flora of China. Beijing: The Science Publishing Company.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

