Pooled-analysis of tadalafil and tamsulosin for ureteral calculi
- PMID: 38873423
- PMCID: PMC11169629
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1351312
Pooled-analysis of tadalafil and tamsulosin for ureteral calculi
Abstract
Objective: Urolithiasis is a common urological diseases and affects the daily life of patients. Medical expulsive therapy has become acceptable for many parents. We conducted a meta-analysis to determine the efficacy and safety of tadalafil compared with tamsulosin for treating distal ureteral stones less than 10 mm in length.
Methods: Related studies were identified via searches of the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. All the articles that described the use of tadalafil and tamsulosin for treating distal ureteral stones were collected.
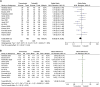
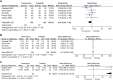
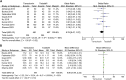
Results: A total of 14 studies were included in our meta-analysis. Our results revealed that tadalafil enhanced expulsion rate [odds ratio (OR) = 0.68, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.47 to 0.98, p = 0.04]; reduced expulsion time [mean difference (MD) = 1.22, 95% CI (0.13, 2.30), p = 0.03]; lowered analgesia use [MD = 38.66, 95% CI (7.56, 69.77), p = 0.01] and hospital visits [MD = 0.14, 95% CI (0.06, 0.22), p = 0.0006]. According to our subgroup analysis, either tadalafil 5 mg or 10 mg did not promote expulsion rate and accelerate expulsion time compared with tamsulosin. But patients receiving 5 mg tadalafil decreased analgesia usage [MD = 101.04, 95% CI (67.56, 134.01), p < 0.00001].
Conclusion: Compared with tamsulosin, tadalafil demonstrates a higher expulsion rate and less expulsion time for patients with distal ureteral stones less than 10 mm with a favorable safety profile.
Keywords: distal ureteral calculi; meta-analysis; prospective randomized trials; tadalafil; tamsulosin.
Copyright © 2024 Sun, Liu, Wu, Liu, Liu, Wang, Zou, Cui and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tadalafil Facilitates the Distal Ureteral Stone Expulsion: A Meta-Analysis.J Endourol. 2017 Jun;31(6):557-563. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0837. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Endourol. 2017. PMID: 28384011 Review.
-
Comparing efficacy and safety of monotherapy and combination therapy with tadalafil, tamsulosin, and silodosin for distal ureteral stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian J Urol. 2025 Apr;12(2):189-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2024.05.003. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Asian J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40458580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tamsulosin vs. Tadalafil as medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Braz J Urol. 2023 Nov-Dec;49(6):668-676. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2023.0345. Int Braz J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37903004 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil versus alpha blockers (alfuzosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin and silodosin) as medical expulsive therapy for < 10 mm distal and proximal ureteral stones.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018 Jun 30;90(2):117-122. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2018.2.117. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018. PMID: 29974727
-
Meta-Analysis of the Safety and Efficacy of α-Adrenergic Blockers for Pediatric Urolithiasis in the Distal Ureter.Front Pediatr. 2022 Apr 15;10:809914. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.809914. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35498769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abhishek L., Shashikant M., Arvind G., Ravindra S., Mahesh D. (2015). Comparison of tadalafil and tamsulosin in medical expulsive therapy for ureteric calculus: prospective, randomized, placebo controlled study. Indian J. Urology 31, S39.
-
- Boulos V., Nada A. J. E. U. S. (2018). Is medical expulsive therapy (MET) with tadalafil more effective than tamsulosin in distal ureteric stones (DUS)? A prospective randomized study. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 17, e923. 10.1016/s1569-9056(18)31473-8 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

