The efficacy of herbal medicines on the length of stay and negative conversion time/rate outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review
- PMID: 38873430
- PMCID: PMC11169809
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1383359
The efficacy of herbal medicines on the length of stay and negative conversion time/rate outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, diverse initiatives have been carried out to control the COVID-19 pandemic, ranging from measures restricting social activities to analyzing drugs and vaccines. Studies on herbal medicines are also increasingly conducted in various countries as an adjuvant therapy or supplement. Therefore, this systematic review aimed to investigate the efficacy of herbal medicines analyzed from various countries through clinical trials with the randomized controlled trial method. The outcomes of Length of Stay (LOS), Negative Conversion Time (NCT), and Negative Conversion Rate (NCR) were the main focus.
Methods: An extensive review of literature spanning from 2019 to 2023 was carried out using well-known databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane. The search included relevant keywords such as "randomized controlled trial," "COVID-19," and "herbal medicine."
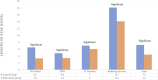
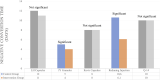
Results: A total of 8 articles were part of the inclusion criteria with outcomes of LOS, NCT, and NCR. In terms of LOS outcomes, all types of herbal medicines showed significant results, such as Persian Medicine Herbal (PM Herbal), Persian Barley Water (PBW), Jingyin Granules (JY granules), Reduning Injection, and Phyllanthus emblica (Amla). However, only JY granules showed significant results in NCR outcome, while JY granules and Reduning Injection showed significant results in reducing NCT.
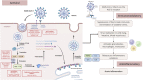
Conclusion: These findings enrich our understanding of the potential benefits of herbal medicines in influencing LOS, NCR and NCT parameters in COVID-19 patients. Herbal medicines worked to treat COVID-19 through antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory mechanisms.
Keywords: antiinflammatory; antiviral; clinical trial; herbal medicines; immunomodulatory; randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2024 Latarissa, Meiliana, Sormin, Sugiono, Wathoni, Barliana and Lestari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amini S. Z., Shakeri N., Amini S. M., Mokaberinejad R., Hasheminasab F. S., Azimi M., et al. (2022). Evaluating the effect of a natural formulation based on hordeum vulgare on the recovery of COVID-19 patients: application of survival analysis in a clinical trial. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. 20, 1–5. 10.5812/AMH-128009 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources