A comparative analysis of the nutrient and phytochemical richness among different varieties of quinoa in China
- PMID: 38873460
- PMCID: PMC11167139
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4113
A comparative analysis of the nutrient and phytochemical richness among different varieties of quinoa in China
Abstract
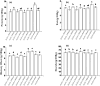
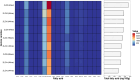
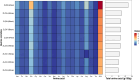
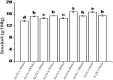
Quinoa is a nutrient-dense pseudocereal that has garnered global attention for its potential to bolster food security and nutrition. Despite its celebrated status, the detailed nutritional profiles of various quinoa varieties remain poorly understood, which poses a significant barrier to the strategic cultivation and utilization of quinoa's genetic diversity to combat malnutrition. The impetus for this research lies in the urgent need to identify superior quinoa strains that can be tailored to meet specific nutritional requirements and adapt to diverse agro-ecological zones. Our findings reveal substantial variation in nutrient content across different quinoa varieties, highlighting the variety ZLZX-8 as a particularly nutrient-rich strain with the highest levels of protein, fat, essential fatty acids, amino acids, and key minerals such as Mg, K, and Zn. Moreover, ZLZX-8's exceptional antioxidant capacity suggests it may have additional health benefits beyond its macronutrient profile. In contrast, ZLZX-7 stands out for its dietary fiber and phenolic content, which are critical for digestive health and disease prevention, respectively. Meanwhile, ZLZX-5, with its high starch content, could be better suited for energy production in dietary applications. Notably, the study also uncovers a correlation between grain color and nutrient profile, with colored quinoa varieties exhibiting superior fiber, inositol, phenolic content, and antioxidant activity compared to their white counterparts. This work lays the groundwork for an informed selection of quinoa varieties that can enhance dietary quality, support local and global food systems, and contribute to the fight against malnutrition.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; germplasm diversity; nutritional composition; quality evaluation; quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa).
© 2024 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of quinoa and food processing on gastrointestinal health: a narrative review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Oct 18:1-14. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2416476. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39422522 Review.
-
Seed Composition and Amino Acid Profiles for Quinoa Grown in Washington State.Front Nutr. 2020 Aug 12;7:126. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00126. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32903386 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the nutritional composition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.).Food Chem. 2016 Feb 15;193:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.111. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26433286
-
Effect of Germination on the Physicochemical Properties, Functional Groups, Content of Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Capacity of Different Varieties of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Grown in the High Andean Zone of Peru.Foods. 2024 Jan 27;13(3):417. doi: 10.3390/foods13030417. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338552 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in physiochemical changes, nutritional value, bioactivities, and food applications of germinated quinoa: A comprehensive review.Food Chem. 2023 Nov 15;426:136390. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136390. Epub 2023 May 15. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37307740 Review.
References
-
- Chen, Z. J. , & Liao, C. S. (2020). Comparative of 7 different varieties of Chenopodium quinoa . Science and Technology of Food Industry, 41(23), 266–271. 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020020197 - DOI
-
- Friedemann, T. E. , & Witt, N. F. (1967). Determination of starch and soluble carbohydrates. II. Collaborative study of starch determination in cereal grains and cereal products. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 50(4), 958–963. 10.1093/jaoac/50.4.958 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

