Peganum harmala L. extract-based Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs): Green synthesis, characterization, and assessment of antibacterial and antifungal properties
- PMID: 38873463
- PMCID: PMC11167161
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4112
Peganum harmala L. extract-based Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs): Green synthesis, characterization, and assessment of antibacterial and antifungal properties
Abstract
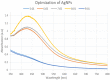
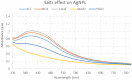
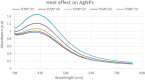
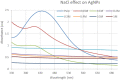
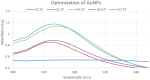
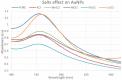
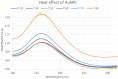
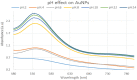
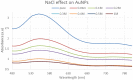
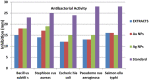
During the last decade, nanotechnology has attained a significant place among the scientific community for the biosynthesis of plant-based nanoparticles owing to its effective, safe, and eco-friendly nature. Hence, keeping in view the significance of nanotechnology, the current study was conducted to develop, characterize (UV-visible spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy), and assess the antimicrobial (antibacterial and antifungal) properties of Peganum harmala L. Extract-based Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs). Characteristic absorption peaks at 420 and 540 nm revealed the formation of AgNPs and AuNPs, respectively. SEM images revealed that both silver and gold nanoparticles were oval and spherical with average size ranging from 42 to 72 and 12.6 to 35.7 nm, respectively. Similarly, FT-IR spectra revealed that the functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and polyphenolic groups of biomolecules present in the extract are possibly responsible for reducing metallic ions and the formation of nanoparticles. Likewise, the EDX analysis confirmed the presence of silver and gold in synthesized NPs. Furthermore, the AgNPs and AuNPs showed good antibacterial and antifungal activities. The maximum antibacterial and antifungal activity was noticed for P. harmala extract against Pseudomonas aeroginosa (21 mm) and Candida albicon (18 mm), respectively. Whereas, the maximum antibacterial and antifungal activities of synthesized AgNPs were observed against Salmonella typhi (25 mm) and Penicillium notatum (36 mm), respectively. Moreover, in the case of AuNPs, the highest antibacterial and antifungal activity of synthesized AuNPs was noticed against Escherichia coli (25 mm) and C. albicon (31 mm), respectively. Findings of this study revealed that P. harmala extract and biosynthesized NPs (silver and gold) possessed significant antibacterial and antifungal properties against different bacterial (Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, P. aeroginosa, and S. typhi) and fungal (C. albicans, Aspergillus Niger, and P. notatum) strains. Further studies must be carried out to assess the probable mechanism of action associated with these antimicrobial properties.
Keywords: Peganum harmala; Ag and Au NPs; antibacterial; antifungal activity.
© 2024 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Green synthesis and bactericidal activities of isotropic and anisotropic spherical gold nanoparticles produced using Peganum harmala L leaf and seed extracts.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019 Jul;66(4):664-672. doi: 10.1002/bab.1782. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31141208
-
Characterization and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Potential of Trigonella incise (Linn) Mediated Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2022 Jul 20;27(14):4618. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144618. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889490 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver, Copper, and Ag-Cu Bimetallic Nanoparticles Using Peganum harmala Demonstrating Advanced Catalytic, Antioxidant, and Biomedical Applications.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;197(6):3630-3667. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05186-4. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39964595
-
Green synthesis, characterization of silver nanoparticals for biomedical application and environmental remediation.J Microbiol Methods. 2022 Feb;193:106384. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106384. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Microbiol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34826520 Review.
-
Algal production of nano-silver and gold: Their antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities: A review.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2016 Dec;14(2):299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Oct 6. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 30647628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Past to Present: Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) in Daily LifeSynthesis Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, Characterization, Toxicity, and Emerging Applications in Biomedicine, Nanoelectronics, and Materials Science.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 30;10(31):33999-34087. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03162. eCollection 2025 Aug 12. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40821590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustainable Nanotechnology Strategies for Modulating the Human Gut Microbiota.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5433. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125433. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro biological activities of silver nanoparticles using methanolic leaf extract of Plumeria rubra.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 3;15(1):28303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14353-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40754561 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Doped Antibacterial and Antifungal Coatings.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;17(2):247. doi: 10.3390/polym17020247. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the preparation of sterile noble metal nanoparticles and hydrotalcite layered nanoparticles by innovative high pressure sterilization method.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 27;15(1):14711. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99577-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40289210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu‐Tahon, M. A. , Ghareib v, M. , & Abdallah, W. E. (2020). Environmentally benign rapid biosynthesis of extracellular gold nanoparticles using Aspergillus flavus and their cytotoxic and catalytic activities. Process Biochemistry, 95, 1–11. 10.1016/j.procbio.2020.04.015 - DOI
-
- Adebayo, E. , Ishola, O. , Taiwo, O. , Majolagbe, O. , & Adekeye, B. (2009). Evaluations of the methanol extract of Ficus exasperata stem bark, leaf and root for phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activities. African Journal of Plant Science, 3(12), 283–287.
-
- Ahmad, S. , Ali, M. , Ansari, S. H. , & Ahmed, F. (2010). Phytoconstituents from the galls of Pistacia integerrima Stewart. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 14(4), 409–412. 10.1016/j.jscs.2010.05.003 - DOI
-
- Alhumaydhi, F. A. , Khan, I. , Rauf, A. , Qureshi, M. N. , Aljohani, A. S. , Khan, S. A. , Khalil, A. A. , El‐Esawi, M. A. , & Muhammad, N. (2021). Synthesis, characterization, biological activities, and catalytic applications of alcoholic extract of saffron (Crocus sativus) flower stigma‐based gold nanoparticles. Green Processing and Synthesis, 10(1), 230–245. 10.1515/gps‐2021‐0024 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

