A comprehensive review: Impact of oleogel application on food texture and sensory properties
- PMID: 38873467
- PMCID: PMC11167145
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4110
A comprehensive review: Impact of oleogel application on food texture and sensory properties
Abstract
Oleogels, characterized by their semisolid matrix formed from liquid oil structured by gelators, are emerging as a pivotal innovation in food formulation, primarily due to their capacity to enhance the nutritional profile of products by incorporating healthier fats. This review explored the integration of oleogels into diverse food matrices, examining their impact on texture, mouthfeel, and overall sensory characteristics. Through an extensive analysis of current research, this paper illustrates the versatility of oleogels created with a variety of structuring agents across different food applications. It also addresses the challenges inherent in the use of oleogels, including the preservation of their stability and consistency through varying storage and processing conditions, navigating the regulatory landscape concerning oleogelator safety and acceptability, and confronting higher production costs. Overall, this comprehensive review highlights the potential of oleogels as a promising tool for achieving desirable textural and sensory attributes in food products while also identifying areas for future research and development.
Keywords: oleogel; oleogel‐based food; saturated fat replacer; sensory; texture.
© 2024 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between authors.
Figures

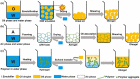
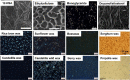
References
-
- Adrah, K. , Adegoke, S. C. , Nowlin, K. , & Tahergorabi, R. (2021). Study of oleogel as a frying medium for deep‐fried chicken. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 16(2), 1114–1123. 10.1007/s11694-021-01237-6 - DOI
-
- Afoakwa, E. O. (2016). Chocolate science and technology. John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Airoldi, R. , da Silva, T. L. T. , Ract, J. N. R. , Foguel, A. , Colleran, H. L. , Ibrahim, S. A. , & da Silva, R. C. (2022). Potential use of carnauba wax oleogel to replace saturated fat in ice cream. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 99(11), 1085–1099. 10.1002/aocs.12652 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

