Brexucabtagene autoleucel for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in the United Kingdom: A real-world intention-to-treat analysis
- PMID: 38873532
- PMCID: PMC11170269
- DOI: 10.1002/hem3.87
Brexucabtagene autoleucel for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in the United Kingdom: A real-world intention-to-treat analysis
Abstract
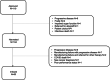
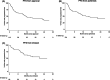
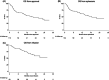
Brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexu-cel) is an autologous CD19 CAR T-cell product, approved for relapsed/refractory (r/r) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). In ZUMA-2, brexu-cel demonstrated impressive responses in patients failing ≥2 lines, including a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with an overall and complete response rate of 93% and 67%, respectively. Here, we report our real-world intention-to-treat (ITT) outcomes for brexu-cel in consecutive, prospectively approved patients, from 12 institutions in the United Kingdom between February 2021 and June 2023, with a focus on feasibility, efficacy, and tolerability. Of 119 approved, 104 underwent leukapheresis and 83 received a brexu-cel infusion. Progressive disease (PD) and/or manufacturing (MF) were the most common reasons for failure to reach harvest and/or infusion. For infused patients, best overall and complete response rates were 87% and 81%, respectively. At a median follow-up of 13.3 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) for infused patients was 21 months (10.1-NA) with a 6- and 12-month PFS of 82% (95% confidence interval [CI], 71-89) and 62% (95% CI, 49-73), respectively. ≥Grade 3 cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity occurred in 12% and 22%, respectively. On multivariate analysis, inferior PFS was associated with male sex, bulky disease, ECOG PS > 1 and previous MF. Cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (NRM) was 6%, 15%, and 25% at 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively, and mostly attributable to infection. Outcomes for infused patients in the UK are comparable to ZUMA-2 and other real-world reports. However, ITT analysis highlights a significant dropout due to PD and/or MF. NRM events warrant further attention.
© 2024 The Authors. HemaSphere published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Hematology Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Maeve A. O'Reilly: honoraria from Kite Gilead, Novartis, and Janssen. Advisory boards Kite Gilead and Autolus. Conference/travel support Kite Gilead. William Wilson: No COI. David Burns: Kite Gilead consultancy fees and support for educational meetings. Andrea Kuhnl: Kite Gilead conference support, honoraria, advisory board, Novartis: honoraria, research funding, Advisory board: Roche, Abbvie, BMS. Frances Seymour: No COI. Ben Uttenthal: No COI. Caroline Besley: Honoraria: Kite, Janssen, Novartis and Takeda. Rajesh Alajangi: No COI. Thomas Creasey: No COI. Shankara Paneesha: No COI. Johnathon Elliot: No COI. Carlos Gonzalez Arias: Kite Gilead conference support, honoraria, advisory board, research funding; Novartis conference support, honoraria, advisory board; BMS advisory board. Sunil Iyengar: conference support Beigene, BMS, Takeda. Speaker fees Kite Gilead, Takeda. Advisory boards Kite, MSD. Matthew R. Wilson: Honoraria/speaker fees: Kite/Gilead, Janssen, Sobi, Takeda, Veriton Pharma, AstraZeneca, Roche. Conference/travel support: Gilead, Janssen, Kite, Takeda, AstraZeneca. Alison Delaney: Kite Gilead conference support. Lourdes Rubio: No COI. Jonathan Lambert: advisory boards: Kite‐Gilead and Blueprint Pharmaceuticals; BMS, Takeda and Novartis: conference support. Khalil Begg: No COI. Stephen Boyle: Honoraria Kite Gilead. Kathleen P. L. Cheok: No COI. Graham P. Collins: Kite Gilead speaker fees, advisory board. Claire Roddie: Advisory boards and speakers fees Novartis, Kite Gilead, BMS, Amgen, Autolus. Rod Johnson: Kite Gilead consultancy fees, support for educational meetings. Robin Sanderson: Kite Gilead speakers bureau, honoraria, conference travel, Novartis speakers bureau, honoraria, conference travel.
Figures



References
-
- Hoster E, Rosenwald A, Berger F, et al. Tumor cell proliferation (Ki‐67 index) overcomes cytology and growth pattern as prognostic factor in mantle cell lymphoma—results from randomized trials of the European MCL network. Blood. 2014;124(21):2977. 10.1182/blood.V124.21.2977.2977 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
