Regulated vascular smooth muscle cell death in vascular diseases
- PMID: 38873710
- PMCID: PMC11533065
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13688
Regulated vascular smooth muscle cell death in vascular diseases
Abstract
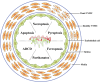
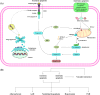
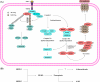
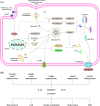
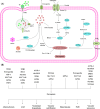
Regulated cell death (RCD) is a complex process that involves several cell types and plays a crucial role in vascular diseases. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are the predominant elements of the medial layer of blood vessels, and their regulated death contributes to the pathogenesis of vascular diseases. The types of regulated VSMC death include apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, parthanatos, and autophagy-dependent cell death (ADCD). In this review, we summarize the current evidence of regulated VSMC death pathways in major vascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, vascular calcification, aortic aneurysm and dissection, hypertension, pulmonary arterial hypertension, neointimal hyperplasia, and inherited vascular diseases. All forms of RCD constitute a single, coordinated cell death system in which one pathway can compensate for another during disease progression. Pharmacologically targeting RCD pathways has potential for slowing and reversing disease progression, but challenges remain. A better understanding of the role of regulated VSMC death in vascular diseases and the underlying mechanisms may lead to novel pharmacological developments and help clinicians address the residual cardiovascular risk in patients with cardiovascular diseases.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cell Proliferation published by Beijing Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82270454/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000299/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82100292/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82070436/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZNQNJC2023001/Youth Interdisciplinary Special Fund of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

