Target Identification and Mechanistic Characterization of Indole Terpenoid Mimics: Proper Spindle Microtubule Assembly Is Essential for Cdh1-Mediated Proteolysis of CENP-A
- PMID: 38873820
- PMCID: PMC11304278
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305593
Target Identification and Mechanistic Characterization of Indole Terpenoid Mimics: Proper Spindle Microtubule Assembly Is Essential for Cdh1-Mediated Proteolysis of CENP-A
Abstract
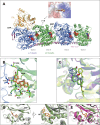
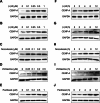
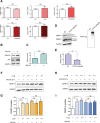
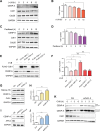
Centromere protein A (CENP-A), a centromere-specific histone H3 variant, is crucial for kinetochore positioning and chromosome segregation. However, its regulatory mechanism in human cells remains incompletely understood. A structure-activity relationship (SAR) study of the cell-cycle-arresting indole terpenoid mimic JP18 leads to the discovery of two more potent analogs, (+)-6-Br-JP18 and (+)-6-Cl-JP18. Tubulin is identified as a potential cellular target of these halogenated analogs by using the drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) based method. X-ray crystallography analysis reveals that both molecules bind to the colchicine-binding site of β-tubulin. Treatment of human cells with microtubule-targeting agents (MTAs), including these two compounds, results in CENP-A accumulation by destabilizing Cdh1, a co-activator of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) E3 ubiquitin ligase. This study establishes a link between microtubule dynamics and CENP-A accumulation using small-molecule tools and highlights the role of Cdh1 in CENP-A proteolysis.
Keywords: CENP‐A regulation; Cdh1; colchicine‐binding site inhibitor; indole terpenoid; target identification.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The E3-ligases SCFPpa and APC/CCdh1 co-operate to regulate CENP-ACID expression across the cell cycle.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 23;47(7):3395-3406. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz060. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30753559 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of CENP-R by Aurora B regulates kinetochore-microtubule attachment for accurate chromosome segregation.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Sep 27;14(7):mjac051. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac051. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36069839 Free PMC article.
-
Centromere Dysfunction Compromises Mitotic Spindle Pole Integrity.Curr Biol. 2019 Sep 23;29(18):3072-3080.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.07.052. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31495582
-
The centromere comes into focus: from CENP-A nucleosomes to kinetochore connections with the spindle.Open Biol. 2020 Jun;10(6):200051. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200051. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32516549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leaving no-one behind: how CENP-E facilitates chromosome alignment.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 4;64(2):313-324. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190073. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32347304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Target discovery-directed pharmacological mechanism elucidation of bioactive natural products.Med Rev (2021). 2025 Mar 6;5(4):277-296. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0076. eCollection 2025 Aug. Med Rev (2021). 2025. PMID: 40838108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
