Protective effects of selegiline against amyloid beta-induced anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment
- PMID: 38873869
- PMCID: PMC11176901
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3599
Protective effects of selegiline against amyloid beta-induced anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment
Abstract
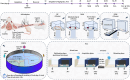
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex and common neurodegenerative disorder. The present study aimed to investigate the potential effects of selegiline (SEL) on various aspects of memory performance, anxiety, and oxidative stress in an AD rat model induced by intracerebroventricular injection of amyloid beta1-42 (Aβ1-42).
Methods: Oral administration of SEL at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day was performed for 30 consecutive days. Following the 30 days, several tests, including the open-field, elevated plus-maze, novel object recognition, Morris water maze, and passive avoidance learning were conducted to assess locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, recognition memory, spatial memory, and passive avoidance memory, respectively.
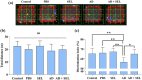
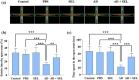
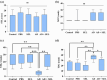
Results: The results indicate that the induction of AD in rats led to recognition memory, spatial memory, and passive avoidance memory impairments, as well as increased anxiety. Additionally, the AD rats exhibited a decrease in total antioxidant capacity and an increase in total oxidant status levels, suggesting an imbalance in oxidative-antioxidant status. However, the administration of SEL improved memory performance, reduced anxiety, and modulated oxidative-antioxidant status in AD rats.
Conclusions: These findings provide evidence that SEL may alleviate anxiety-like behavior and cognitive deficits induced by Aβ through modulation of oxidative-antioxidant status.
Keywords: alzheimer's disease; anxiety; oxidative stress; passive avoidance memory; selegiline; spatial memory.
© 2024 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effects of L-carnitine against beta-amyloid-induced memory impairment and anxiety-like behavior in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 5;982:176879. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176879. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39128806
-
Selegiline Improves Cognitive Impairment in the Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):2548-2560. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04388-x. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39136906
-
Royal jelly improves learning and memory deficits in an amyloid β-induced model of Alzheimer's disease in male rats: Involvement of oxidative stress.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Apr;38(4):1239-1248. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01168-9. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36809522
-
Minocycline effects on memory and learning impairment in the beta-amyloid-induced Alzheimer's disease model in male rats using behavioral, biochemical, and histological methods.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 15;953:175784. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175784. Epub 2023 May 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37179042
-
The Protective Effects of Policosanol on Learning and Memory Impairments in a Male Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 May;60(5):2507-2519. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03225-x. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36680733
Cited by
-
Beta-Amyloid and Its Asp7 Isoform: Morphological and Aggregation Properties and Effects of Intracerebroventricular Administration.Brain Sci. 2024 Oct 21;14(10):1042. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14101042. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39452054 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement in modeling of Alzheimer's disease: a comprehensive review of preclinical screening platforms.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Aug 6;17:1646551. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1646551. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40842652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cacao Ameliorates Amyloid Beta-Induced Cognitive and Non-Cognitive Disturbances.Neurosci Insights. 2024 Sep 17;19:26331055241280638. doi: 10.1177/26331055241280638. eCollection 2024. Neurosci Insights. 2024. PMID: 39314637 Free PMC article.
-
Aging-Associated Amyloid-β Plaques and Neuroinflammation in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and Novel Cognitive Health-Supporting Roles of Pentadecanoic Acid (C15:0).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 16;26(8):3746. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083746. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadi, N. , Mirazi, N. , Komaki, A. , Safari, S. , & Hosseini, A. (2021). Vanillic acid attenuates amyloid β1‐40‐induced long‐term potentiation deficit in male rats: An in vivo investigation. Neurological Research, 43, 562–569. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi, N. , Safari, S. , Mirazi, N. , Karimi, S. A. , & Komaki, A. (2021). Effects of vanillic acid on Aβ1‐40‐induced oxidative stress and learning and memory deficit in male rats. Brain Research Bulletin, 170, 264–273. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, A. B. , & Chetia, P. (2023). MAO–B inhibitor “selegiline” attenuates oxidative stress and arthritic parameters in an invitro repurposed studies. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 40(2), 171–181. - PubMed
-
- Arib, O. , Rat, P. , Molimard, R. , Chait, A. , Faure, P. , & de Beaurepaire, R. (2010). Electrophysiological characterization of harmane‐induced activation of mesolimbic dopamine neurons. European Journal of Pharmacology, 629(1–3), 47–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

