A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Split-Face, Comparative Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of DKL23 and Juvéderm Volift for Correcting Moderate-to-Severe Nasolabial Folds
- PMID: 38874166
- PMCID: PMC11474605
- DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjae133
A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Split-Face, Comparative Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of DKL23 and Juvéderm Volift for Correcting Moderate-to-Severe Nasolabial Folds
Abstract
Background: Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers are used for multiple indications, including wrinkle correction and restoration of volume/fullness.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of 2 hyaluronic acid products for correcting moderate to severe nasolabial folds (NLFs).
Methods: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, split-face study was undertaken. The subjects' left and right NLFs were randomly allocated for treatment with DKL23 or Juvéderm Volift. Follow-up was conducted at 1, 3, 6, and 9 months. The changes from baseline on the Wrinkle Severity Rating Scale and the Global Aesthetics Improvement Scale were evaluated. Posttreatment adverse events (AEs) were recorded.
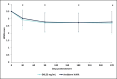
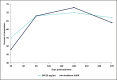
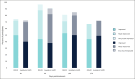
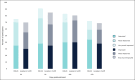
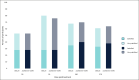
Results: Forty-eight women (median age, 57.0 years) with Type I to VI skin were enrolled. Both treatments showed statistically significant improvement (P < .0001) in NLFs according to the Wrinkle Severity Rating Scale score from baseline to each of the time points assessed. The improvement in NLFs was maintained until the end of the study (9 months). Furthermore, the change from baseline to each of the time points assessed was similar between DKL23 and Juvéderm Volift. Investigator- and subject-rated Global Aesthetics Improvement Scale scores showed similar rates of improvement (indicated by the sum of responses of improved, much improved, or very much improved) between the 2 products. The AEs reported in the study were in line with previous and expected experience after injection of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. The types of AEs, their rates, intensity, and duration were comparable between the 2 products.
Conclusions: DKL23 improved NLF severity from baseline and for up to 9 months, and the results were comparable to the improvement shown by Juvéderm Volift. Treatment was safe and well tolerated.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

