MASH as an emerging cause of hepatocellular carcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives
- PMID: 38874196
- PMCID: PMC11793012
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13685
MASH as an emerging cause of hepatocellular carcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives
Abstract
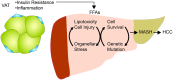
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the deadliest and fastest-growing cancers. Among HCC etiologies, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) has served as a major HCC driver due to its great potential for increasing cirrhosis. The obesogenic environment fosters a positive energy balance and results in a continuous rise of obesity and metabolic syndrome. However, it is difficult to understand how metabolic complications lead to the poor prognosis of liver diseases and which molecular mechanisms are underpinning MAFLD-driven HCC development. Thus, suitable preclinical models that recapitulate human etiologies are essentially required. Numerous preclinical models have been created but not many mimicked anthropometric measures and the course of disease progression shown in the patients. Here we review the literature on adipose tissues, liver-related HCC etiologies and recently discovered genetic mutation signatures found in MAFLD-driven HCC patients. We also critically review current rodent models suggested for MAFLD-driven HCC study.
Keywords: ER stress; Hepatocellular carcinoma; MASH; genetic mutation; inflammation; lipotoxicity; metabolic syndrome; obesity.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- El‐Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S27–S34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical